Sunstone Configuration¶
Important
You are in the Legacy Components section of the documentation. The pages in this section refer to components currently included in OpenNebula, but which are no longer maintained or receive bug fixes; they will be removed in future versions. For information on the latest changes in OpenNebula, please refer to the Release Notes.
The OpenNebula Sunstone server provides a web-based management interface. It’s a dedicated daemon installed by default as part of the Single Front-end Installation, but can be deployed independently on a different machine. The server is distributed as an operating system package opennebula-sunstone with the system services opennebula-sunstone for Sunstone and opennebula-novnc for noVNC Proxy.
Configuration¶
The Sunstone configuration file can be found in /etc/one/sunstone-server.conf on your Front-end. It uses YAML syntax with following parameters:
Note
After a configuration change, the Sunstone server must be restarted to take effect.
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Server Configuration |
|
|
Directory for the temporary storage of uploaded images before copying to OpenNebula
(Default: |
|
Endpoint of OpenNebula XML-RPC API (Default: |
|
Timeout (in seconds) for XML-RPC calls from Sunstone. See Shell Environment variables. |
|
Endpoint for ZeroMQ subscriptions (Default: |
|
Hostname/IP where server will listen (Default: |
|
Port where server will listen (Default: |
|
Method of keeping user sessions. It can be |
|
Hostname/IP of memcached server (only for memcached-based sessions) (Default: |
|
Port of memcached server (only for memcached-based sessions) (Default: |
|
Memcached namespace to store sessions, useful when memcached is used by other services
(Default: |
|
Execution environment for Sunstone. With |
|
Maximum permitted size of uploaded images (in bytes). Leave commented for unlimited size |
Logging |
|
|
Logging level. Values: |
Proxy |
|
|
Proxy server for HTTP traffic |
|
Patterns for IP addresses or domain names that shouldn’t use the proxy |
Authentication |
|
|
Authentication driver for incoming requests. Possible values are |
|
Authentication driver to communicate with OpenNebula Daemon. Possible values are |
|
Two Factor Authentication Issuer Label (Default: |
WebAuthn |
|
|
|
|
Relying Party name for display purposes (Default: |
|
Time (in ms) the browser should wait for any interaction with user (Default: |
|
Optional differing Relying Party ID |
|
List of supported cryptographic algorithms. Options: |
Upgrades Checks |
|
|
URL to check for latest releases (Default: |
UI Settings |
|
|
Base port for the noVNC proxy. Can be prefixed with an address on which the sever will
be listening (ex: 127.0.0.1:29876). (Default: |
|
Values |
|
Full path to certificate file for WSS connections. |
|
Full path to key file. Not necessary if key is included in certificate. |
|
Enable IPv6 for noVNC - |
|
Port where the noVNC JS client will connect.
If not set, will use the port section of |
|
Request VNC password for external windows, |
|
Display VNC icons in federation, |
|
Login Session Length in seconds (Default: |
|
Enable option ‘Keep me logged in’ in Sunstone login (Default: |
|
Default language for the Sunstone interface. This is the default language that will
be used if user has not defined a variable |
|
Default table order. Resources get ordered by ID in |
|
Default Sunstone views group (Default: |
|
True to display extended VM information from OpenNebula (Default: |
|
True to display extended information from VM monitoring from OpenNebula (Default: |
|
Array for paginate, the first position is for internal use. The second is used to put names to each value. |
|
Displays button and clock icon in table of VM |
|
Disable the information sending via URL to Guacamole console |
|
Minimum percentage value for green color on thresholds |
|
Minimum percentage value for orange color on thresholds |
|
Minimum percentage value for red color on thresholds |
|
Default interval for timestamps. THIS VALUE CANNOT BE LOWER THAN EXPIRE_MARGIN. |
|
Tokens will be generated if time > EXPIRE_TIME - EXPIRE_MARGIN |
|
List of filesystems to offer when creating new Image |
Official Support |
|
|
Customer token to contact support from Sunstone |
Marketplace |
|
|
Username credential to connect to the Marketplace |
|
Password to connect to the Marketplace |
|
Endpoint to connect to the Marketplace. If commented, a 503 |
OneFlow |
|
|
Endpoint to connect to the OneFlow server (Default: |
Routes |
|
|
List of Ruby files containing custom routes to be loaded. Check server plugins for more information. |
FireEdge |
|
|
Base URL (hostname/IP-based) where the FireEdge server is running.
This endpoint must be reachable by Sunstone server.
(Default: |
|
Base URL (hostname/IP-based) where the FireEdge server is running.
This endpoint must be reachable by end-users!
(Default: |
Note
To disable using fireedge you can set both of the endpoints to be '' which will cause sunstone to fall back to the noVNC server for VNC access
:private_fireedge_endpoint: ''
:public_fireedge_endpoint: ''
In order to properly use Sunstone with FireEdge in HA environments and have the Guacamole functionality available, all Sunstone servers need to access /var/lib/one/.one/fireedge_key.
Note
To use Sunstone on IPv6-only environments with thin HTTP server, use the full IPv6 address in the configuration parameter :host. If you need to set the localhost address (::1) or the unspecified address (::), use one of the following examples:
:host: 0::1
:host: 0::0
Sunstone settings can be also configured on user-level through the user template (within a SUNSTONE=[] section, for example SUNSTONE=[TABLE_ORDER="asc"]). The following attributes are available for customization:
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Name of the user that will appear in Sunstone |
|
Values |
|
Name of the default view (as located in |
|
Default length of Sunstone datatables’ pages |
|
Sunstone language (defaults to en_US) |
|
Default zone at Sunstone login. Defaults to the local zone. |
Configure FireEdge¶
Optional FireEdge server provides the additional functionality to Sunstone:
Remote access VMs using Guacamole and/or VMRC (VMware Remote Console). FireEdge acts as a proxy between Sunstone and hypervisor nodes or vCenter/ESX (see more) and streaming the remote console/desktop of the Virtual Machines.
Sunstone has to be configured (/etc/one/sunstone-server.conf) with two FireEdge endpoints to work properly:
:private_fireedge_endpoint- base URL reachable by Sunstone (leave default if running on same host),:public_fireedge_endpoint- base URL reachable by end-users.
Both values can be same, as long as they are valid. For example:
:private_fireedge_endpoint: http://f2.priv.example.com:2616
:public_fireedge_endpoint: http://one.example.com:2616
Hint
If you are not planning to use FireEdge, you can disable it by commenting both endpoints in configuration:
#:private_fireedge_endpoint: http://localhost:2616
#:public_fireedge_endpoint: http://localhost:2616
If FireEdge is running on a different host, the cipher key /var/lib/one/.one/fireedge_key for Guacamole connections must be copied among Hosts.
Service Control and Logs¶
Manage operating system services opennebula-sunstone and opennebula-novnc to change the server(s) running state.
To start, restart or stop the server, execute one of:
systemctl start opennebula-sunstone
systemctl restart opennebula-sunstone
systemctl stop opennebula-sunstone
To enable or disable automatic start on Host boot, execute one of:
systemctl enable opennebula-sunstone
systemctl disable opennebula-sunstone
Note
noVNC Proxy Server is automatically started (unless masked) when OpenNebula Sunstone starts.
Servers logs are located in /var/log/one in following files:
/var/log/one/sunstone.log/var/log/one/sunstone.error/var/log/one/novnc.log
Other logs are also available in Journald; use the following command to show these:
journalctl -u opennebula-sunstone.service
journalctl -u opennebula-novnc.service
Usage¶
Commercial Support Integration¶
We are aware that in production environments, access to professional, efficient support is a must and this is why we have introduced an integrated tab in Sunstone to access OpenNebula Systems (the company behind OpenNebula, formerly C12G) professional support. In this way, support ticket management can be performed through Sunstone, avoiding disruption of work and enhancing productivity.
Troubleshooting¶
Failed to Connect to OneFlow¶
The Service and Service Template tabs may complain about connection failures to the OneFlow server (Cannot connect to OneFlow server). E.g.:
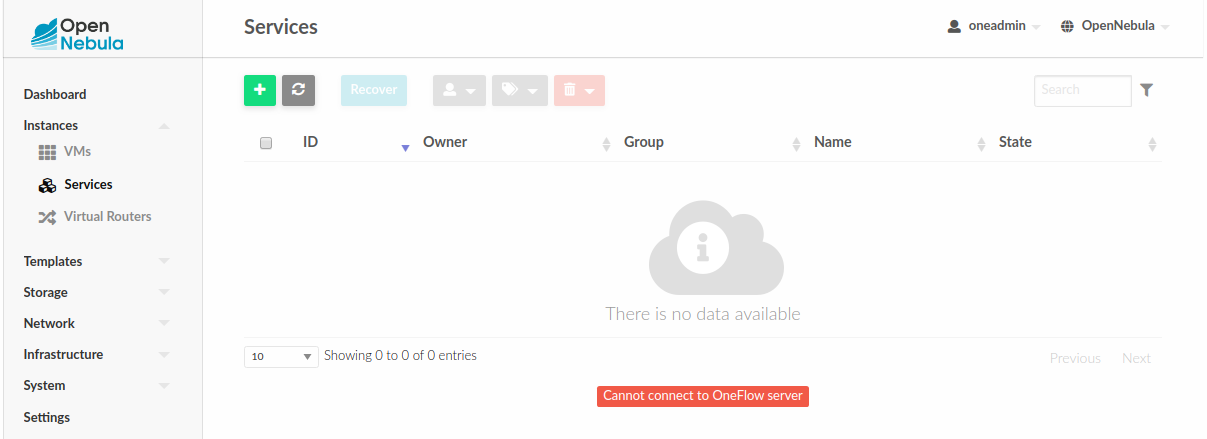
Ensure you have OneFlow server configured and running, or disable Service and Service Templates tabs in Sunstone View.
Tuning and Extending¶
Internationalization and Localization¶
Sunstone supports multiple languages. If you want to contribute a new language, make corrections, or complete a translation, you can visit our Transifex project page. Translating through Transifex is easy and quick. All translations should be submitted via Transifex.
Users can update or contribute translations any time. Prior to every release, normally after the beta release, a call for translations will be made in the forum. Then the source strings will be updated in Transifex so all the translations can be updated to the latest OpenNebula version. Translations with an acceptable level of completeness will be added to the final OpenNebula release.
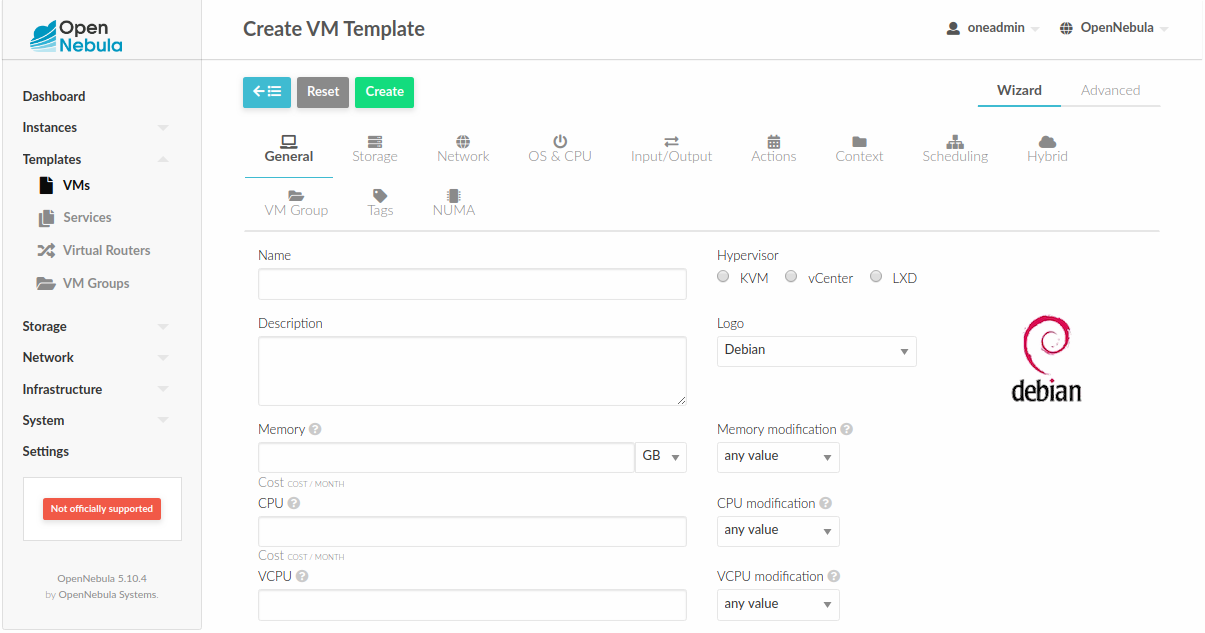
Customize VM Logos¶
The VM Templates can have an image logo to identify the guest OS. Edit /etc/one/sunstone-logos.yaml to modify the list of available logos. Example:
- { 'name': "Alpine Linux", 'path': "images/logos/alpine.png"}
- { 'name': "ALT", 'path': "images/logos/alt.png"}
- { 'name': "Arch Linux", 'path': "images/logos/arch.png"}
- { 'name': "Debian", 'path': "images/logos/debian.png"}
- { 'name': "Fedora", 'path': "images/logos/fedora.png"}
- { 'name': "FreeBSD", 'path': "images/logos/freebsd.png"}
- { 'name': "HardenedBSD", 'path': "images/logos/hardenedbsd.png"}
- { 'name': "Knoppix", 'path': "images/logos/knoppix-logo.png"}
- { 'name': "Linux", 'path': "images/logos/linux.png"}
- { 'name': "Oracle", 'path': "images/logos/oel.png"}
- { 'name': "Redhat", 'path': "images/logos/redhat.png"}
- { 'name': "SUSE", 'path': "images/logos/suse.png"}
- { 'name': "Ubuntu", 'path': "images/logos/ubuntu.png"}
- { 'name': "Windows XP/2003", 'path': "images/logos/windowsxp.png"}
- { 'name': "Windows 8/2012", 'path': "images/logos/windows8.png"}
- { 'name': "Windows 10/2016", 'path': "images/logos/windows8.png"}
Guest OS logo as shown in Sunstone:
Branding Sunstone¶
You can add your logo to the login and main screens by updating the logo: attribute as follows:
The login screen is defined in the
/etc/one/sunstone-views.yaml.The logo of the main UI screen is defined for each view in the view yaml file.
The logo image must be copied to /usr/lib/one/sunstone/public/images/.
You can also change the color threshold values in the /etc/one/sunstone-server.conf.
The green color starts in
:threshold_min:The orange color starts in
:threshold_low:The red color starts in
:threshold_high:
Global User Settings of Sunstone Views¶
OpenNebula Sunstone can be adapted to different user roles. For example, it will only show the resources the users have access to. Its behavior can be customized and extended via Sunstone Views.
The preferred method to select which views are available to each group is to update the group
configuration from Sunstone, as described in Sunstone Views section.
There is also the /etc/one/sunstone-views.yaml file that defines an alternative method to
set the view for each user or group.
Sunstone will offer the available views to each user in the following way:
From all the groups the user belongs to, the views defined inside each group are combined and presented to the user.
If no views are available from the user’s group, the defaults are taken from
/etc/one/sunstone-views.yaml. Here, views can be defined for:Each user (
users:section): list each user and the set of views available for him or her.Each group (
groups:section): list the set of views for the group.The default view: if a user is not listed in the
users:section, nor its group in thegroups:section, the default views will be used.The default views for group admins: if a group admin user is not listed in the
users:section, nor its group in thegroups:section, the default_groupadmin views will be used.
By default, users in the oneadmin group have access to all views, and users in the users
group can use the cloud view.
The following example of /etc/one/sunstone-views.yaml enables the user (user.yaml) and the
cloud (cloud.yaml) views for user helen and the cloud (cloud.yaml) view for group cloud-users. If more
than one view is available for a given user, the first one is the default.
---
logo: images/opennebula-sunstone-v4.0.png
users:
helen:
- cloud
- user
groups:
cloud-users:
- cloud
default:
- user
default_groupadmin:
- groupadmin
- cloud
Different Endpoint for Different View¶
OpenNebula Sunstone Views can be adapted to use a different endpoint for each kind of user, such as if you want one endpoint for the admins and a different one for the cloud users. You just have to deploy a new sunstone server and set a default view for each sunstone instance:
# Sunstone for Admins
cat /etc/one/sunstone-server.conf
...
:host: admin.sunstone.com
...
cat /etc/one/sunstone-views.yaml
...
users:
groups:
default:
- admin
# Sunstone for Users
cat /etc/one/sunstone-server.conf
...
:host: user.sunstone.com
...
cat /etc/one/sunstone-views.yaml
...
users:
groups:
default:
- user
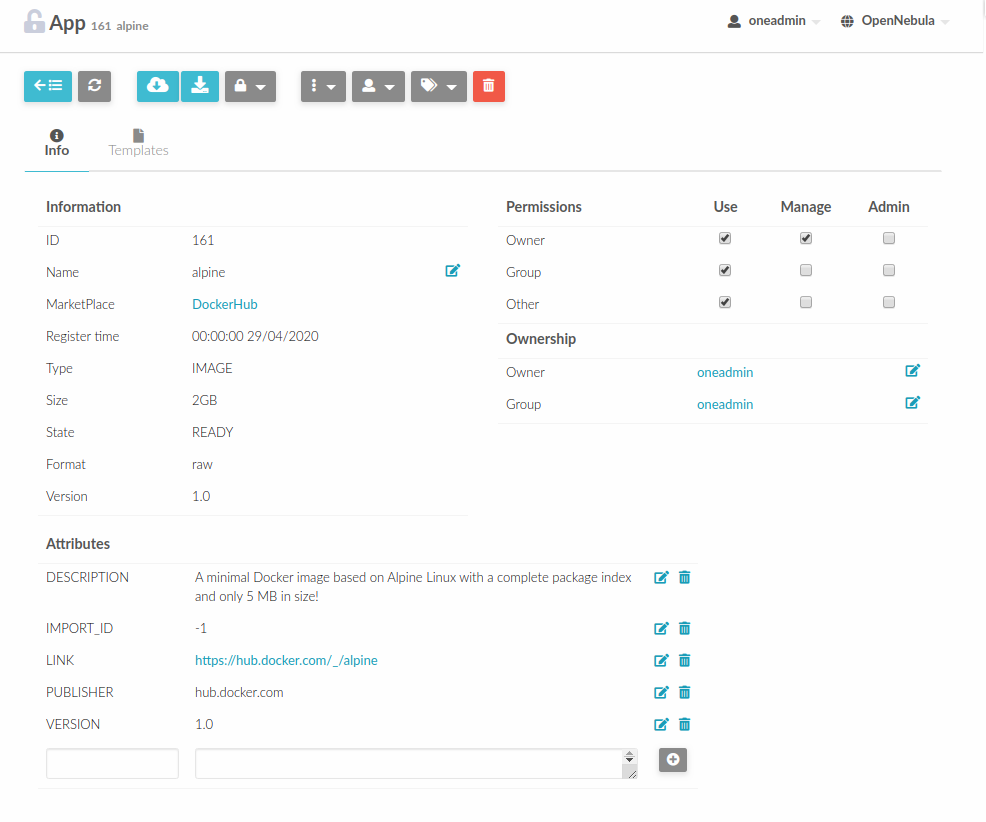
Hyperlinks in Templates¶
Editable template attributes are in various places on Sunstone, for example in the details of Marketplace Appliance. You can add an attribute with the name LINK that contains an URL. The value will be automatically transformed into the clickable hyperlink.