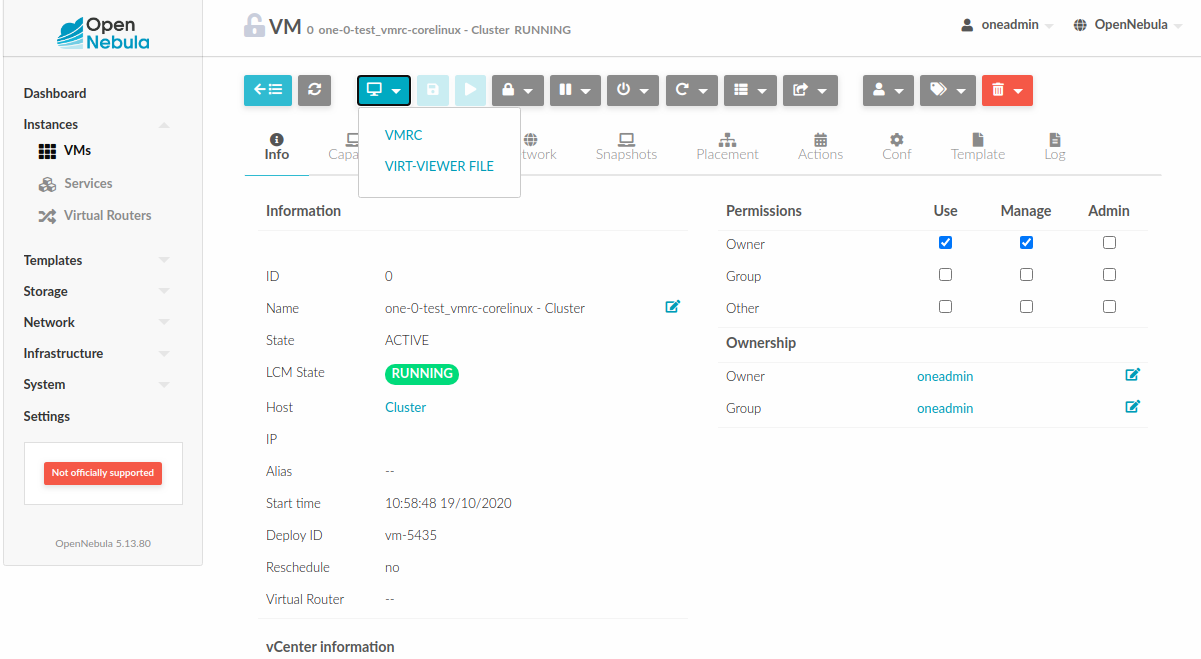
Accessing VM Console and Desktop¶
Sunstone provides several different methods to access your VM console and desktop: VNC, SPICE, RDP, VMRC, SSH, and virt-viewer. If configured in the VM, these methods can be used to access the VM console through Sunstone. For some of those connections, we will need to start a new FireEdge server to establish the remote connection. This section shows how these different technologies can be configured and what each requirement is.
FireEdge automatically installs dependencies for Guacamole connections and VMRC proxy, which are necessary to use VNC, RDP, SSH, and VMRC.
Connection |
With FireEdge |
Without FireEdge |
|---|---|---|
VNC |
Guacamole |
noVNC |
RDP |
Guacamole |
noVNC |
SSH |
Guacamole |
N/A |
SPICE |
noVNC |
noVNC |
|
noVNC |
noVNC |
VMRC |
VMRC proxy |
N/A |
Important
FireEdge server must be running to get Guacamole connections working. For VMRC, Sunstone and FireEdge must be running on the same server.
Requirements for connections via noVNC¶
The Sunstone GUI offers the possibility of starting a VNC/SPICE session to a Virtual Machine. This is done by using a VNC/SPICE websocket-based client (noVNC) on the client side and a VNC proxy translating and redirecting the connections on the server side.
To enable VNC/SPICE console service, you must have a GRAPHICS section in the VM template, as
stated in the documentation. Make sure the attribute IP is set correctly (0.0.0.0 to allow
connections from everywhere), otherwise no connections will be allowed from the outside.
For example, to configure this in the Virtual Machine template:
GRAPHICS=[
LISTEN="0.0.0.0",
TYPE="vnc"
]
Make sure there are no firewalls blocking the connections and websockets enabled in your browser.
The proxy will redirect the websocket data from the VNC proxy port to the VNC port stated in
the template of the VM. The value of the proxy port is defined in sunstone-server.conf as
:vnc_proxy_port.
You can retrieve useful information from /var/log/one/novnc.log. Your browser must support
websockets, and have them enabled.
When using secure websockets, make sure that your certificate and key (if not included in the certificate) are correctly set in the Sunstone configuration files. Note that your certificate must be valid and trusted for the wss connection to work.
If you are working with a certificate that is not accepted by the browser, you can manually add
it to the browser trust list by visiting https://sunstone.server.address:vnc_proxy_port.
The browser will warn that the certificate is not secure and prompt you to manually trust it.
Configuring your VM for VNC¶
VNC is a graphical console with wide support among many hypervisors and clients.
VNC without FireEdge¶
When clicking the VNC icon a request is made, and if a VNC session is possible, the Sunstone server will add the VM
Host to the list of allowed vnc session targets and create a random token associated with it. The
server responds with the session token, then a noVNC dialog pops up.
The VNC console embedded in this dialog will try to connect to the proxy, either using websockets (default) or emulating them using Flash. Only connections providing the right token will be successful. The token expires and cannot be reused.
Make sure that you can connect directly from the Sunstone Front-end to the VM using a normal VNC
client tool, such as vncviewer.
VNC with FireEdge¶
To enable the VNC console service you must have a GRAPHICS section in the VM template,
as stated in the documentation.
To configure it via Sunstone, you need to update the VM template. In the Input/Output tab, you can see the graphics section where you can add the IP, the port, a connection password or define your keymap.
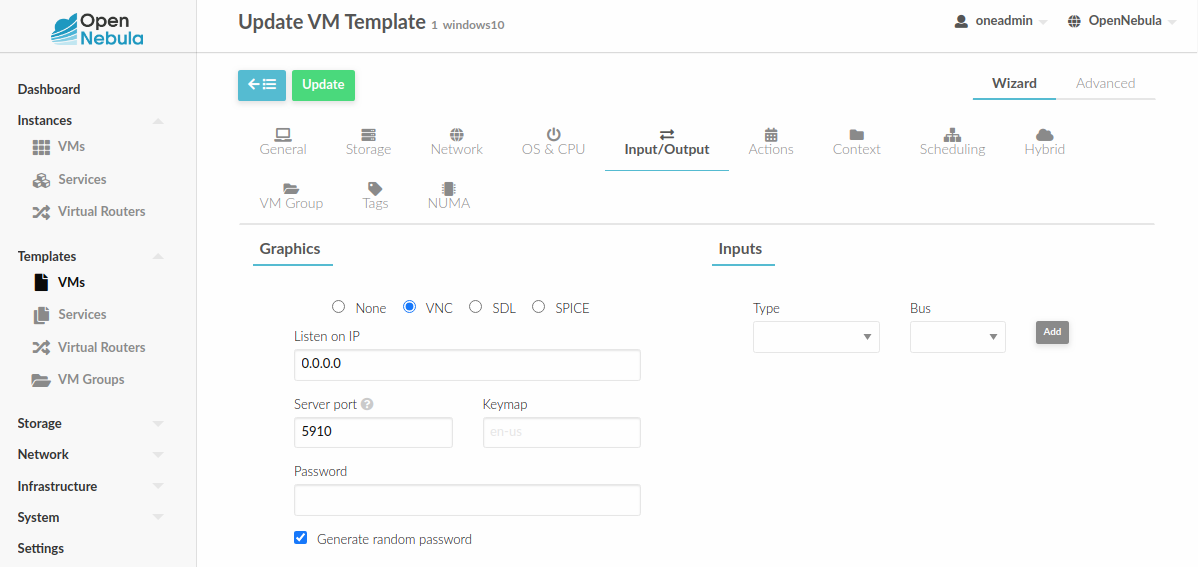
To configure this in Virtual Machine template in advanced mode:
GRAPHICS=[
LISTEN="0.0.0.0",
TYPE="vnc"
]
Note
Make sure the attribute IP is set correctly (0.0.0.0 to allow connections
from everywhere), otherwise, no connections will be allowed from the outside.
Configure VM for RDP¶
Short for Remote Desktop Protocol, it allows one computer to connect to another computer over a network in order to use it remotely.
RDP without FireEdge¶
RDP connections are available on Sunstone using noVNC. You will only have to download the RDP file and open it with an RDP client to establish a connection with your Virtual Machine.
RDP with FireEdge¶
To enable RDP connections to the VM, you must have one NIC
with RDP attribute equal to YES in the template.
Via Sunstone, you need to enable a RDP connection on one of the VM template networks, after or before its instantiation.
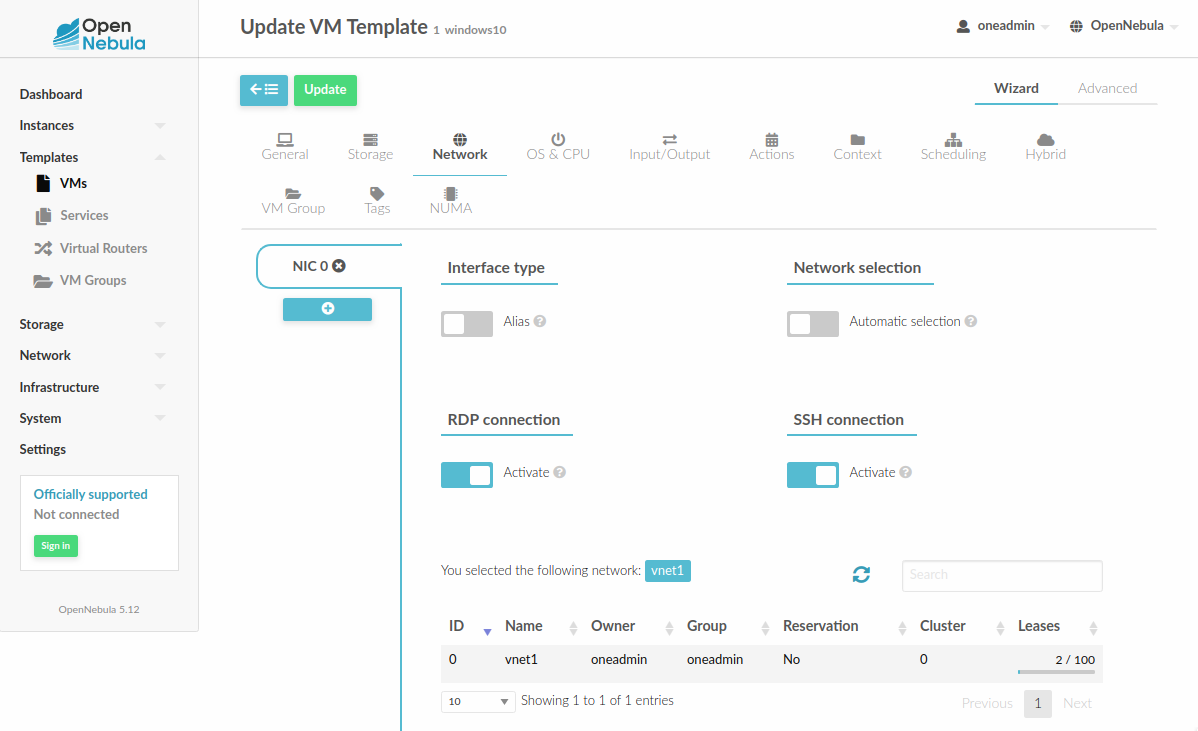
To configure this in Virtual Machine template in advanced mode:
NIC=[
...
RDP = "YES"
]
Once the VM is instantiated, users will be able to download the file configuration or connect via browser.
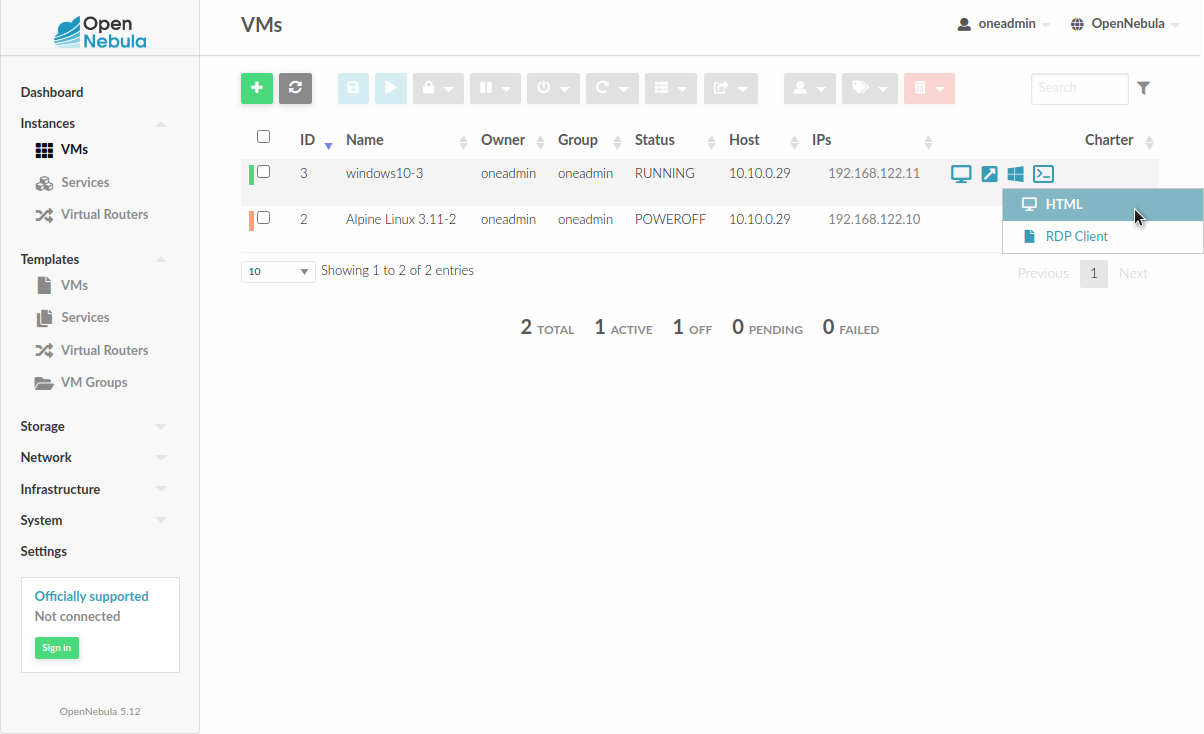
RDP connection permits to choose the screen resolution from Sunstone interface.
Important
The RDP connection is only allowed to activate on a single NIC. In any case, the connection will only contain the IP of the first NIC with this property enabled. The RDP connection will work the same way for NIC ALIASES.
If the VM template has a PASSWORD and USERNAME set in the contextualization section, this will be reflected in the RDP connection. You can read about them in the Virtual Machine Definition File reference section.
Note
If your Windows VM has a firewall enabled, you can set the following in the start script of the VM (in the Context section of the VM Template):
`
netsh advfirewall firewall set rule group="Remotedesktop" new enable=yes
`
Configure VM for SSH¶
SSH connections are available only when a reachable Firedge server is found. Unlike VNC or RDP, SSH is a text protocol. SSH connections require a hostname or IP address defining the destination machine. Like with the RDP connections, you need to enable the SSH connection on one of the VM template networks.
For example, to configure this in the Virtual Machine template in advanced mode:
NIC=[
...
SSH = "YES"
]
SSH is standardized to use port 22 and this will be the proper value in most cases. You only
need to specify the SSH port in the contextualization section as SSH_PORT if you are
not using the standard port.
Note
If the VM template has a PASSWORD and USERNAME set in the contextualization
section, this will be reflected in the SSH connection. You can read about them in the
Virtual Machine Definition File reference section.
For example, to allow connection by username and password to a guest VM, first make sure you have SSH root access to the VM, check more info here.
After that you can access the VM and configure the SSH service:
oneadmin@frontend:~$ ssh root@<guest-vm>
# Allow authentication with password: PasswordAuthentication yes
root@<guest-VM>:~$ vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
# Restart SSH service
root@<guest-VM>:~$ service sshd restart
# Add user: username/password
root@<guest-VM>:~$ adduser <username>
Note
Guacamole SSH uses RSA encryption. Make sure the VM SSH accepts RSA, otherwise you need to explicitly enable it in the VM SSH configuration (HostkeyAlgorithms and PubkeyAcceptedAlgorithms set as ‘+ssh-rsa)
Configure VM for SPICE¶
SPICE connections are channeled only through the noVNC proxy. SPICE support in Sunstone share a similar architecture to the VNC implementation. Sunstone use a SPICE-HTML5 widget in its console dialog that communicates with the proxy by using websockets.
Important
SPICE connections when using NAT and remote-viewer won’t work since noVNC proxy does not offer SPICE support, and a direct connection between browser and virtualization node is needed. However the SPICE HTML5 console can use noVNC proxy to offer SPICE connectivity, please use this option as an alternative
Note
For the correct functioning of the SPICE Web Client, we recommend defining by default
the SPICE parameters in /etc/one/vmm_mad/vmm_exec_kvm.conf. In this way, once the file is modified and OpenNebula is restarted, it will be applied to all the VMs instantiated from now on. You can also override these SPICE parameters in VM Template. For more info check Driver Defaults section.
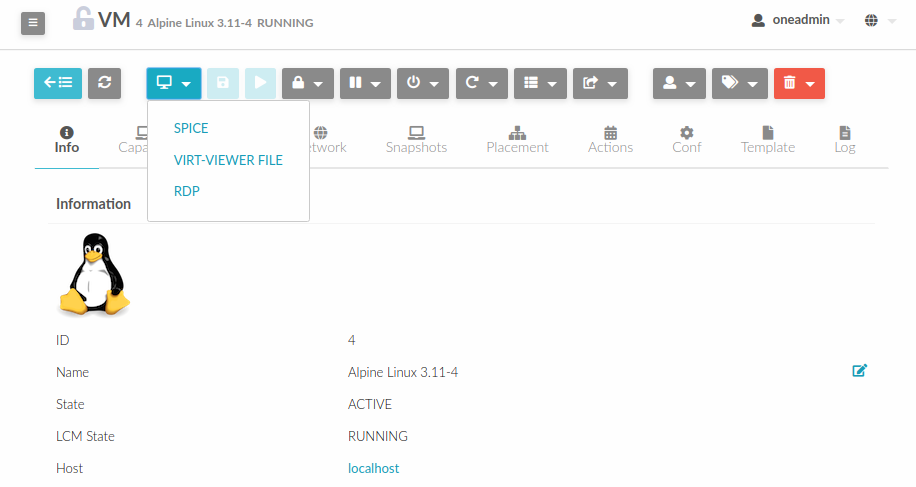
Configure VM for virt-viewer¶
virt-viewer connections are channeled only through the noVNC proxy. virt-viewer is a minimal tool
for displaying the graphical console of a virtual machine. It can display VNC or SPICE protocol,
and uses libvirt to look up the graphical connection details.
In this case, Sunstone allows you to download the virt-viewer configuration file for the VNC and
SPICE protocols. The only requirement is the virt-viewer being installed on the machine from which you are accessing the Sunstone.
To use this option, you will only have to enable any of two protocols in the VM. Once the VM is
instantiated and running, users will be able to download the virt-viewer file.
Configure VM for VMRC¶
Important
VMRC connections are available only when a reachable FireEdge server is found.
VMware Remote Console provides console access and client device connection to VMs on a remote host.
These types of connections request a TOKEN from vCenter to connect with the Virtual Machine
allocated on vCenter every time you click on the VMRC button.
To use this option, you will only have to enable VNC / VMRC connections to your VMs and start the FireEdge Server.
Note
To change the keyboard distribution in the VMRC connection, you need to change the keyboard layout in the running operating system.