OpenNebula Overview¶
Welcome to OpenNebula, the open source Cloud & Edge Computing Platform bringing real freedom to your Enterprise Cloud 🚀
This page provides a high-level overview of the OpenNebula cloud model, architecture and components. To familiarize yourself with OpenNebula and build an evaluation environment, we strongly recommend you follow the tutorials in our Quick Start Guide. For a description of the steps needed to build a production environment, please refer to Cloud Architecture Design.
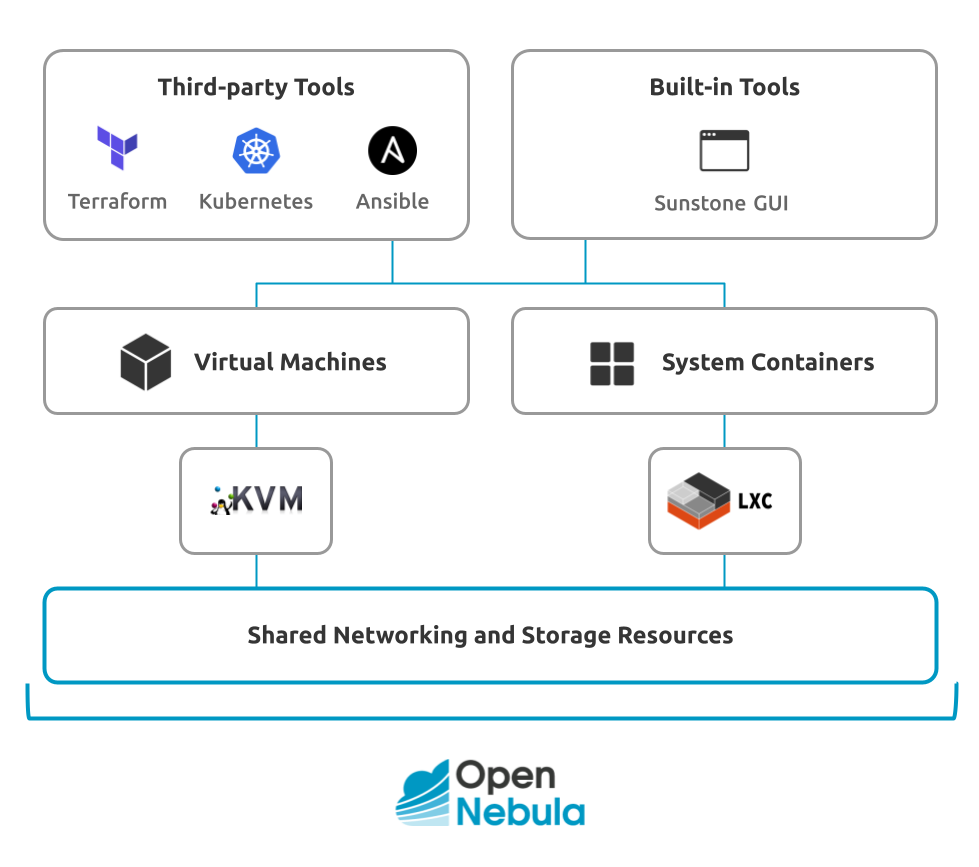
OpenNebula is a powerful, but easy-to-use, open source platform to build and manage enterprise clouds and virtualized Data Centers. It combines existing virtualization technologies with advanced features for multi-tenancy, automatic provision and elasticity on private, hybrid, and edge environments. It unifies management of IT infrastructure and applications, preventing vendor lock-in and reducing complexity, resource consumption and operational costs.
OpenNebula Infrastructure and Management¶
An OpenNebula infrastructure can be deployed on-premises, in the cloud, at the edge, or in hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Virtualization is based on the KVM open source hypervisor, with support for LXC. Cloud resources are orchestrated by one or more OpenNebula Front-ends. The Front-end executes and interacts with components such as daemons, services and interfaces to provide deployment, management, orchestration and monitoring of infrastructure resources. It persists the state of the cloud on a designated SQL database. The system is modular and designed for flexibility; it offers numerous possibilities for deploying the infrastructure as well as the management layer itself, such as support for different database backends, external authentication systems and integration with accounting, chargeback or other platforms.
Virtualized Applications¶
OpenNebula can manage both single VMs and complex multi-tier services composed of several VMs that require sophisticated elasticity rules and dynamic adaptability. Elements in the OpenNebula infrastructure—such as Virtual Machines, networks and appliances—are created from images and templates. Users can modify existing templates or create new ones. Cloud administrators can share templates across their organizations, either directly or using a private corporate marketplace. Additionally, the OpenNebula Public Marketplace offers pre-defined, fully-functional templates for download and deployment, including for multi-VM applications and virtual devices.
Containerized Applications through Kubernetes¶
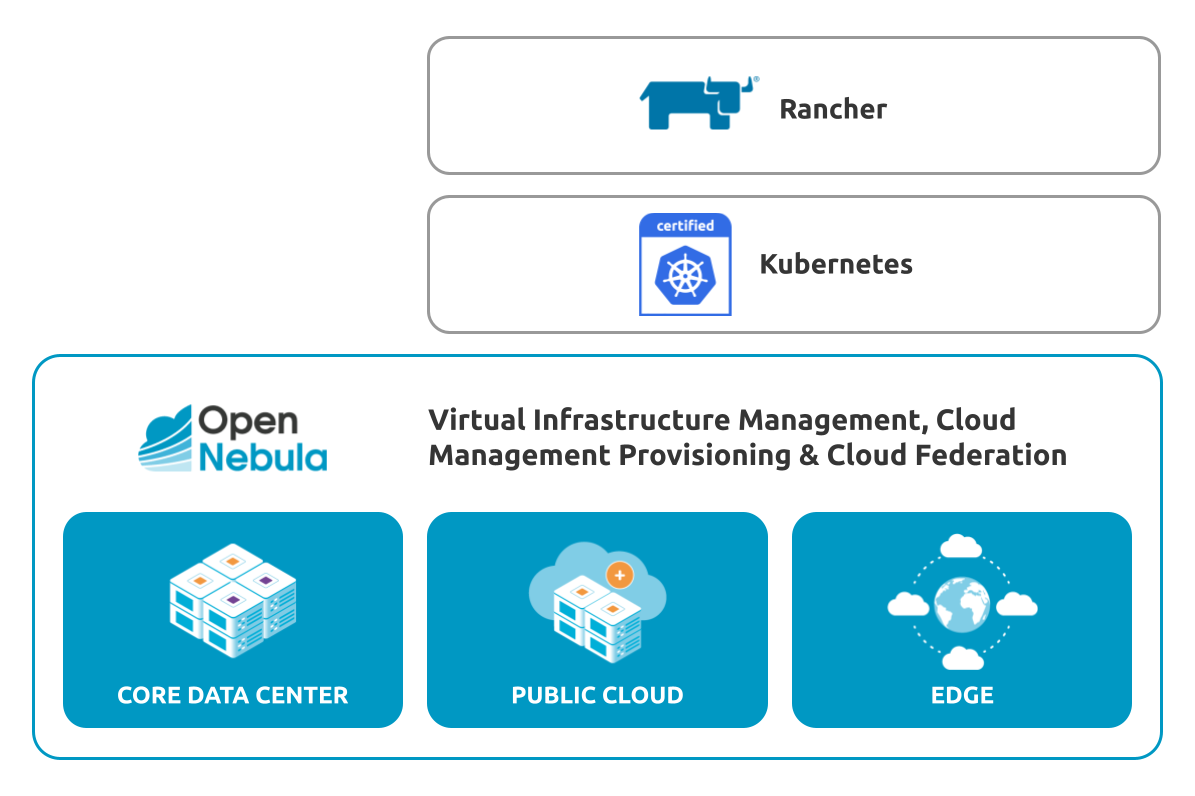
OpenNebula supports the automated deployment of Kubernetes clusters through a virtual appliance, OneKE, the OpenNebula Kubernetes Engine. OneKE is an enterprise-grade, CNCF-certified Kubernetes distribution based on SUSE Rancher RKE2. In its basic configuration it comprises four Virtual Machines: the Kubernetes master node, a VNF node, a storage and a worker node. It can be configured as a multi-master cluster for high availability, and easily scaled up to include more worker nodes, either before deployment or dynamically during operation, by using elasticity rules. It includes features such as MetalLB load balancing, Multus and Cilium CNI plugins, and Longhorn storage. It is available as a multi-VM appliance on the OpenNebula Marketplace, and can be installed in minutes using Sunstone, OpenNebula’s web UI.
Management Model and Tools¶
OpenNebula’s management model provides multi-tenancy by design, offering different user interfaces depending on users’ roles within an organization, or the level of required expertise or functionality.
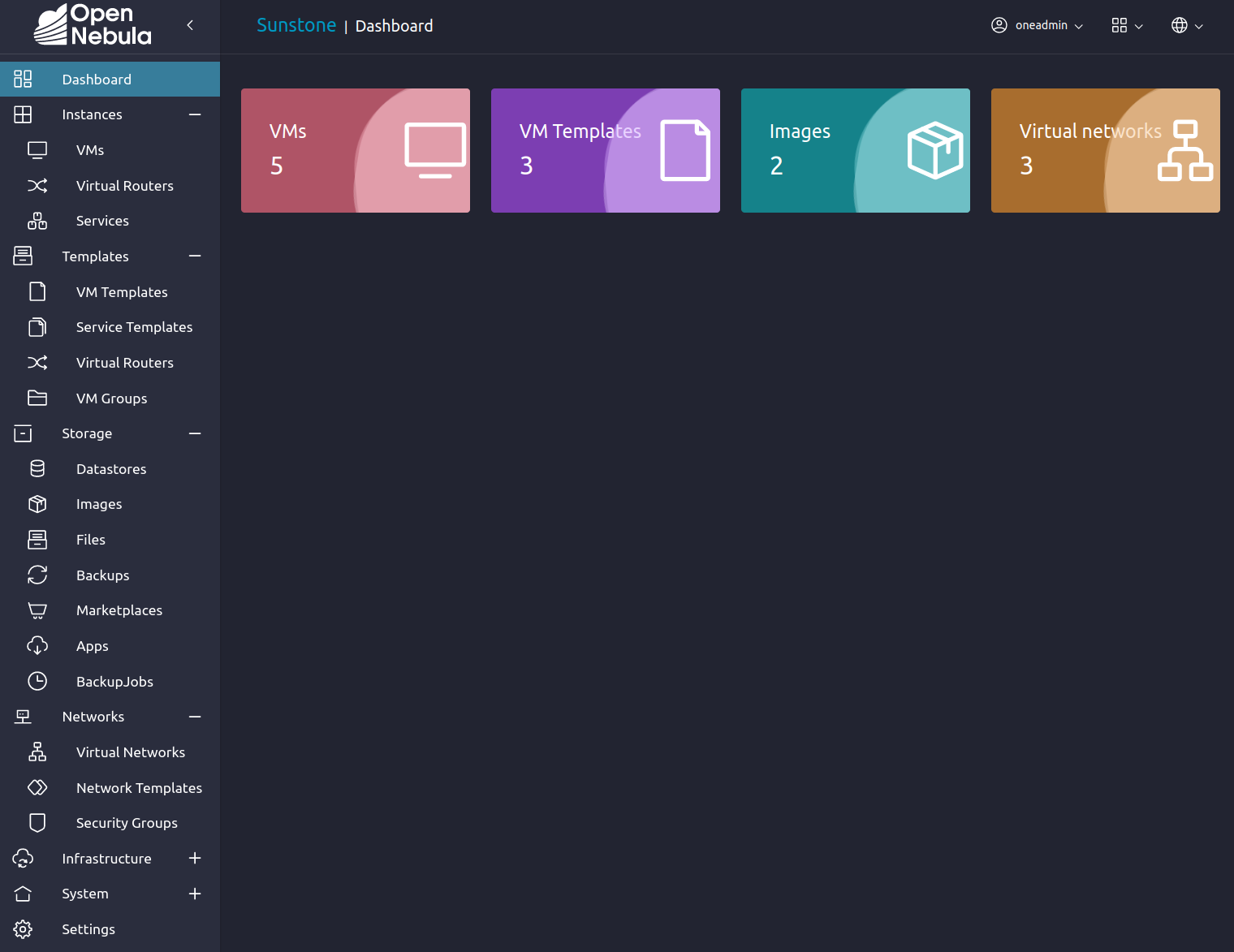
Management tools include the Sunstone Web UI, an easy-to-use visual interface for managing cloud infrastructure. The UI implements the full multi-tenancy features of the underlying system, allowing access to users with different roles, access and management permissions.
Among other features, Sunstone offers support for easily managing single VMs and multi-VM services, as well as datastores, hosts and clusters; visualizing metrics and logs; and creating and editing templates for VMs, services, networks and devices.
Cloud Access Models and Roles¶
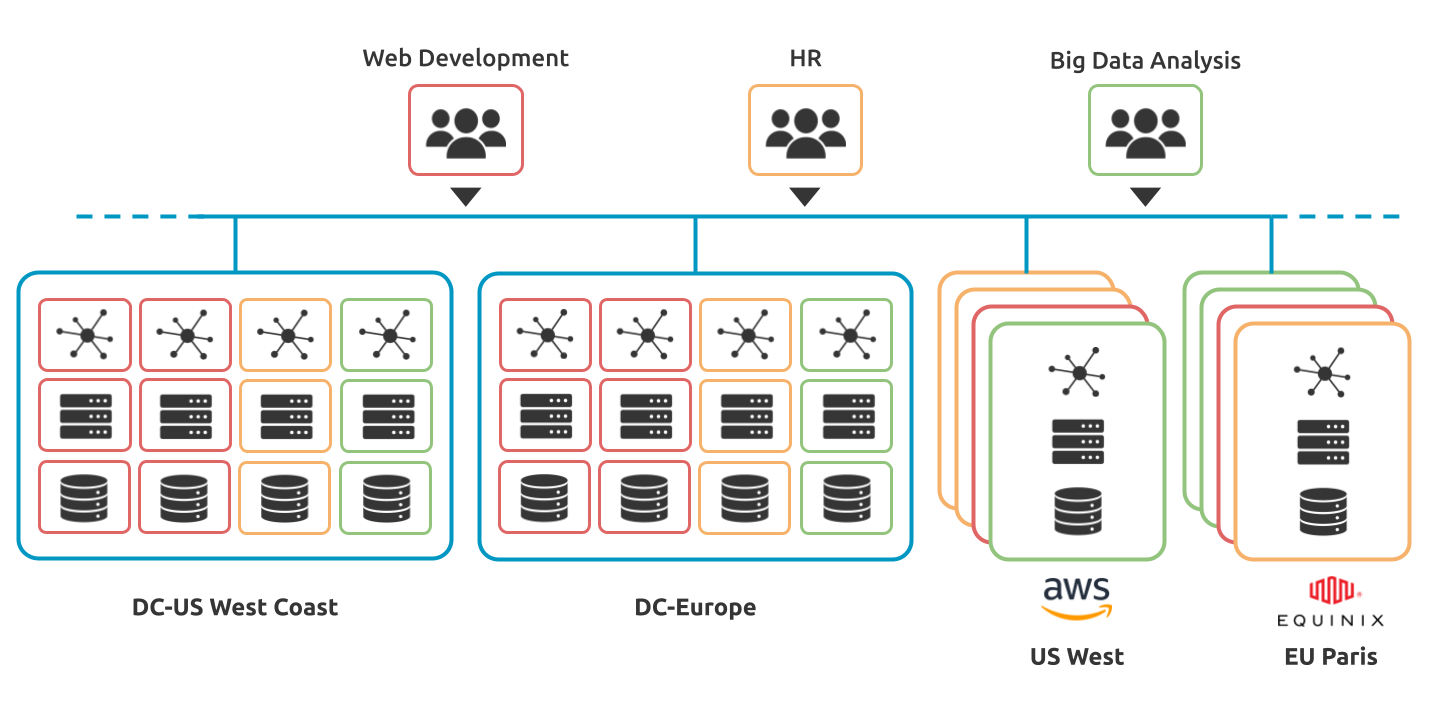
OpenNebula’s cloud provisioning model is based on Virtual Data Centers (VDCs), designed to dynamically provision infrastructure resources in large multi-data center and multi-cloud environments to different customers, business units or groups. The following are common examples of enterprise use cases in large cloud computing environments:
On-premises Private Clouds serving multiple Projects, Departments, Units or Organizations; which require fine-grained and flexible mechanisms to manage access privileges to virtual and physical infrastructures, and to dynamically allocate available resources.
Cloud Providers offering customers Virtual Private Cloud Computing, including a fully-configurable and isolated environment over which customers exercise full control and capacity to administer users and resources. These environments combine a public cloud with the control usually found in a personal private cloud system.
A key management task in an OpenNebula infrastructure environment involves determining who can use the cloud administrative interfaces, and what tasks those users are authorized to perform. The person with the role of cloud service administrator is authorized to assign the appropriate rights required by other users. OpenNebula includes three default user roles: cloud users, cloud operators, and cloud administrators. OpenNebula further offers the possibility of designing custom roles. The OpenNebula documentation provides general guidelines and best practices for determining cloud user roles, in Cloud Access Models and Roles.
The OpenNebula Model for Cloud Infrastructure Deployment¶
A standard OpenNebula Cloud Architecture consists of:
The Cloud Management Cluster with the Front-end node(s), and
The Cloud Infrastructure, comprised by one or several workload Clusters with the hypervisor nodes and the storage system.
Infrastructure components may reside at different geographical locations. They are interconnected by multiple networks for internal storage and node management, and for private and public VM communications.
In general, there are two types of Cluster models that can be used with OpenNebula:
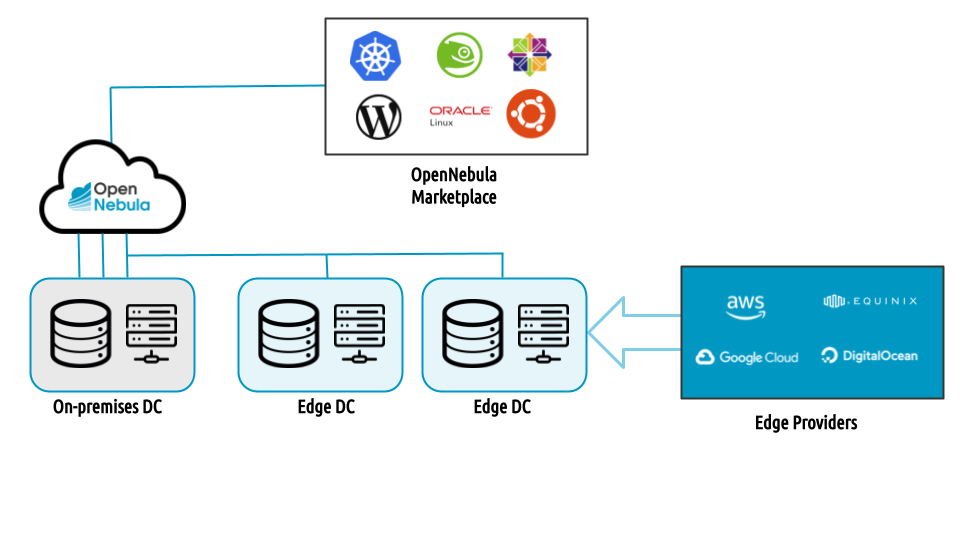
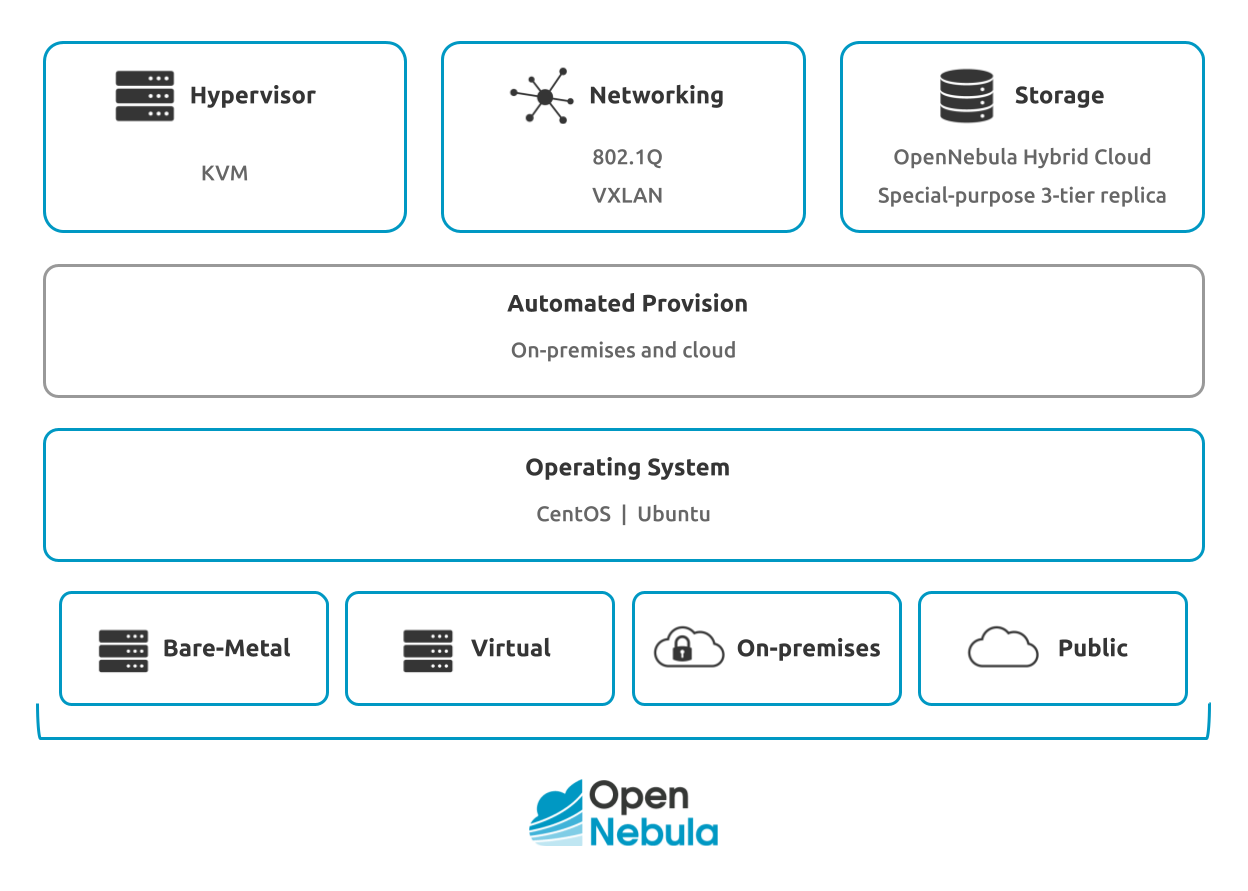
Edge Clusters can be deployed on demand both on-premises and on public cloud and edge providers, with a high degree of integration and automation, to enable seamless hybrid cloud deployments.
Customized Clusters are typically deployed on-premises to meet specific requirements.
Edge Clusters¶
OpenNebula includes its own Edge Cluster configuration. Based on solid open-source storage and networking technologies, OpenNebula’s Edge Cluster model is a much simpler approach than those of customized cloud architectures made of more complex, general purpose and separate infrastructure components. An OpenNebula Edge Cluster can be deployed on-demand on virtual or resources, on premises or on public cloud or edge providers to enable seamless hybrid cloud deployments.
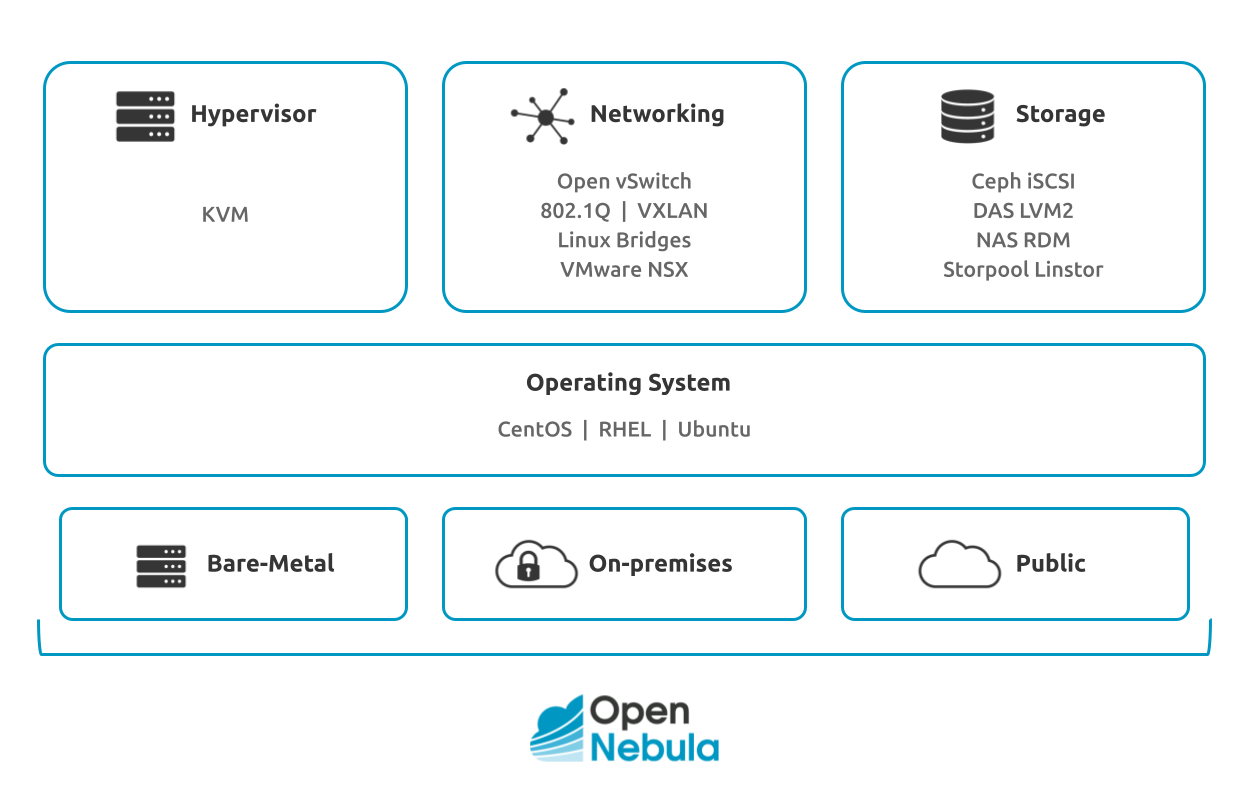
Customized Clusters¶
OpenNebula is certified to work on top of multiple combinations of hypervisors, storage and networking technologies. In this model you need to first install and configure the underlying cloud infrastructure software components, and then install OpenNebula to build the cloud. The clusters can be deployed on-premises or on your choice of bare-metal cloud or hosting provider. While we support OpenNebula and can troubleshoot the cloud infrastructure as a whole, please be aware that in this type of environment you might need to seek commercial support from third-party vendors for the rest of components in your cloud stack.
If you are interested in an OpenNebula cloud fully based on open-source platforms and technologies, please refer to our Open Cloud Reference Architecture.
Choosing the Right Configuration¶
Organizations’ and users’ needs are varied, and constantly evolve over time. We strongly believe that users should be able to choose their own cloud infrastructure configuration, or combination of configurations, that truly helps their business to grow. Our experience working with hundreds of customer engagements shows that our Edge Cluster configuration meets the needs of 90% of their deployments. An OpenNebula Edge Cluster implements enterprise-grade cloud features for performance, availability and scalability with a very simple design that avoids vendor lock-in and reduces complexity, resource consumption and operational costs. Moreover, it enables seamless hybrid cloud deployments that are natively integrated into public clouds. OpenNebula offers a single vendor experience by providing one-stop support and services for your entire cloud stack.
OpenNebula Components¶
OpenNebula was designed to be easily adapted to any infrastructure and easily extended with new components. The result is a modular system that can implement a variety of cloud architectures and interface with multiple data center services.
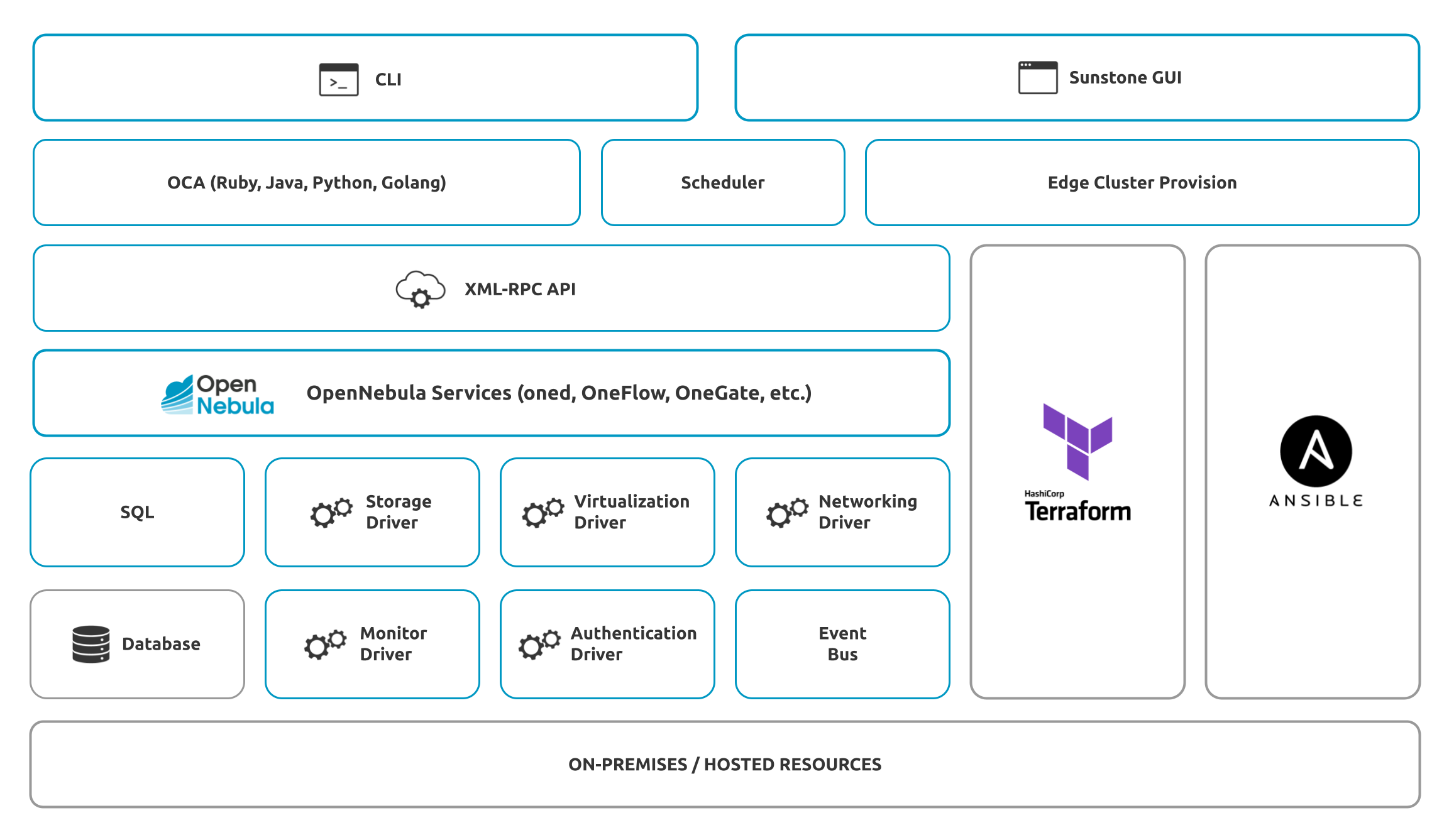
The main components of an OpenNebula installation are listed below.
OpenNebula Daemon (
oned): The OpenNebula Daemon is the core service of the cloud management platform. It manages the cluster nodes, virtual networks and storages, groups, users and their virtual machines; and provides the XML-RPC API to other services and end-users.Database: OpenNebula persists the state of the cloud to a user-selected SQL database. This key component should be monitored and tuned for best performance, following best practices for the particular database product.
Scheduler: The OpenNebula Scheduler is responsible for planning deployment of pending Virtual Machines on available hypervisor nodes. It’s a dedicated daemon (
mm_sched) installed alongside the OpenNebula Daemon, but can be deployed independently on a different machine.Edge Cluster Provision: This component creates fully functional OpenNebula Clusters on public cloud or edge providers. The Provision module integrates Edge Clusters into your OpenNebula cloud by utilizing these three core technologies: Terraform, Ansible and the OpenNebula Services.
Monitoring Subsystem: The monitoring subsystem is implemented as a dedicated daemon (
onemonitord) launched by the OpenNebula Daemon. It gathers information relevant to the Hosts and the Virtual Machines, such as Host status, basic performance indicators, Virtual Machine status and capacity consumption.OneFlow: The OneFlow service orchestrates multi-VM services as single entities, defining dependencies and auto-scaling policies for the application components. It interacts with the OpenNebula Daemon to manage the Virtual Machines (starts, stops), and can be controlled via the Sunstone GUI or over the CLI. It’s a dedicated daemon installed by default as part of the Single Front-end Installation, but can be deployed independently on a different machine.
OneGate: The OneGate server allows Virtual Machines to pull and push information from/to OpenNebula, enabling users and admins to gather metrics, detect problems in their applications, and trigger OneFlow elasticity rules from inside the VMs. It’s a dedicated daemon installed by default as part of the Single Front-end Installation, but can be deployed independently on a different machine.
These are OpenNebula’s system interfaces:
Sunstone: OpenNebula’s next-generation Graphical User Interface (WebUI) intended for both end-users and administrators to easily manage all OpenNebula resources and perform typical operations. It’s a dedicated daemon installed by default as part of the Single Front-end Installation, but can be deployed independently on a different machine.
CLI: OpenNebula includes a comprehensive set of Unix-like command-line tools to interact with the system and its different components.
XML-RPC API: This is the primary interface for OpenNebula, through which you can control and manage any OpenNebula resource, including VMs, Virtual Networks, Images, Users, Hosts, and Clusters.
OpenNebula Cloud API: The OCA provides a simplified and convenient way to interface with the OpenNebula core XML-RPC API, including support for Ruby, Java, Golang, and Python.
OpenNebula OneFlow API: This is a RESTful service to create, control and monitor services composed of interconnected Virtual Machines with deployment dependencies between them.
The interactions between OpenNebula and the underlying cloud infrastructure are performed by specific drivers. Each one addresses a particular area:
Storage: This OpenNebula core layer abstracts storage operations (e.g. clone or delete) implemented by specific programs, which can be replaced or modified to interface special storage backends and filesystems.
Virtualization: OpenNebula implements interactions with hypervisors by using custom programs to boot, stop or migrate a virtual machine. This allows you to specialize each VM operation so as to perform custom operations.
Monitoring: Monitoring information is also gathered by external probes. You can add additional probes to include custom monitoring metrics that can later be used to allocate virtual machines, or for accounting purposes.
Authorization: OpenNebula can also be configured to use an external program to authorize and authenticate user requests, allowing you to implement any access policy to Cloud resources.
Networking: The hypervisor is also prepared with the network configuration for each Virtual Machine.
Event Bus: A generic message bus where OpenNebula publishes resource events. The message bus is used to synchronize OpenNebula services as well as to integrate custom applications.
The OpenNebula documentation provides a summary of its key features. The Platform Notes list the infrastructure platforms and resources supported by each OpenNebula release. Because OpenNebula leverages the functionality exposed by the underlying platform services, its functionality and performance may be affected by the limitations imposed by those services.
Next Steps¶
Building an Evaluation Environment
To evaluate OpenNebula, we strongly recommend that you follow our Quick Start Guide. The Guide will walk you through a series of tutorials to progressively build infrastructure. All tutorials use the Sunstone UI, and most take under ten minutes to complete.
Following the Guide, you can:
Install an OpenNebula Front-end, then use that Front-end to
Deploy an Edge Cluster, where you will
Deploy a Virtual Machine, and finally
The Quick Start Guide is by far the fastest way to familiarize yourself with OpenNebula.
Setting up a Production Environment
If you are interested in building a production environment, then Cloud Architecture Design is a good resource to explore and consider the available options and choices.
If you are interested in automatic, DevOps-like deployment of a production-ready OpenNebula cloud, please refer to the Automatic Deployment section of the Installation Guide.
Remember that if you need our support at any time, or access to our professional services or to the Enterprise Edition, you can always contact us.