On-Premises Edge Cluster¶
Edge Cluster Types¶
On-Premises metal edge clusters use bare-metal servers in your datacenter. Metal provisions can run the LXC or KVM hypervisors.
On-Premises Edge Cluster Implementation¶
An On-Premises Edge Cluster consists of a set of servers with the following requirements:
Host Subsystem |
Configuration & Requirements |
|---|---|
Operating System |
Ubuntu 20.04 Focal installation. |
SSH is configured in the host to grant root passwordless access with the |
|
Networking |
Configured management interface. The OpenNebula front-end can reach the hosts through this network. |
Separated interface connected to the Internet. VMs will access the Internet through this network. Do not configure any IP address for this interface. |
|
Your network should allow inbound connections to ports 22 (TCP), 179 (TCP) and 8472 (UDP) on the management network. The Internet/Public network should not restrict any access. You can later set Security Groups for your VMs. |
|
Storage |
Hosts should have enough local storage mounted under |
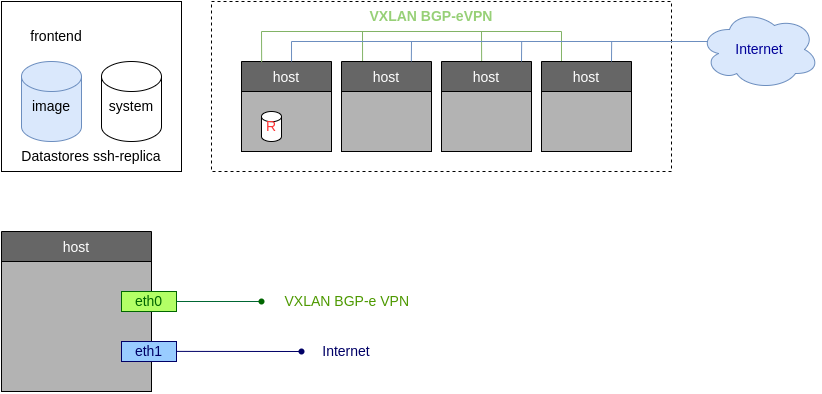
The overall architecture of the On-Premises cluster is shown below.
OpenNebula Resources¶
The following resources, associated to each Edge Cluster, will be created in OpenNebula:
Image and System datastore for the cluster. The storage is configured to use the Hosts local storage through OneStor drivers. On-Premises clusters also include access to the default datastore, so you can easily share images across clusters.
Public Network, bound to the Internet interface through a Linux Bridge.
Private Networking, implemented using a VXLAN overlay on the management network.
Tutorial: Provision an On-Premises Cluster¶
Step 1. Check your Hosts¶
Before we start we need to prepare the hosts for our on-prem cluster. We just need a vanilla installation of Ubuntu Focal with root passwordless SSH access. In this tutorial we’ll use host01 and host02.
ssh root@host01 cat /etc/lsb-release
Warning: Permanently added 'host01,10.4.4.100' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
cat /etc/lsb-release
DISTRIB_ID=Ubuntu
DISTRIB_RELEASE=20.04
DISTRIB_CODENAME=focal
DISTRIB_DESCRIPTION="Ubuntu 20.04.3 LTS"
ssh root@host02 cat /etc/lsb-release
Warning: Permanently added 'host02,10.4.4.101' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
cat /etc/lsb-release
DISTRIB_ID=Ubuntu
DISTRIB_RELEASE=20.04
DISTRIB_CODENAME=focal
DISTRIB_DESCRIPTION="Ubuntu 20.04.3 LTS"
Step 2. Create your On-premises Cluster¶
Check that you have your On-Premises provider created (if not, see above):
oneprovider list
ID NAME REGTIME
0 onprem 04/28 11:31:34
Now we can create our On-Premises Edge Cluster, grab the following attributes for your setup:
Attribute |
Content |
|---|---|
Hostnames |
host01;host02 |
Hypervisor |
LXC |
Public Network Interface |
eth1 |
Public IP block |
172.16.0.2, and the next 10 consecutive addresses |
Private Network Interface |
eth0 |
The command, using a verbose output mode, looks like:
oneprovision create -Dd --provider onprem /usr/share/one/oneprovision/edge-clusters/metal/provisions/onprem.yml
2021-04-28 18:04:45 DEBUG : Executing command: `create`
2021-04-28 18:04:45 DEBUG : Command options: debug [verbose, true] [provider, onprem] [sync, true]
ID: 4
Virtualization technology for the cluster hosts
0 kvm
1 lxc
Please select the option (default=): lxc
Physical device to be used for private networking.
Text `private_phydev` (default=): eth0
Comma separated list of FQDNs or IP addresses of the hosts to be added to the cluster
Array `hosts_names` (default=): host01;host02
Physical device to be used for public networking.
Text `public_phydev` (default=): eth1
First public IP for the public IPs address range.
Text `first_public_ip` (default=): 172.16.0.2
Number of public IPs to get
Text `number_public_ips` (default=1): 10
2021-04-28 18:05:15 INFO : Creating provision objects
...
2021-04-28 18:05:17 DEBUG : Generating Ansible configurations into /tmp/d20210428-3894-z6wb1x
2021-04-28 18:05:17 DEBUG : Creating /tmp/d20210428-3894-z6wb1x/inventory:
[nodes]
host01
host02
[targets]
host01 ansible_connection=ssh ansible_ssh_private_key_file=/var/lib/one/.ssh-oneprovision/id_rsa ansible_user=root ansible_port=22
host02 ansible_connection=ssh ansible_ssh_private_key_file=/var/lib/one/.ssh-oneprovision/id_rsa ansible_user=root ansible_port=22
...
Provision successfully created
ID: 4
Step 3. Quick Tour of your New Cluster¶
Let’s first check the hosts are up and running, in our simple case:
$ onehost list
ID NAME CLUSTER TVM ALLOCATED_CPU ALLOCATED_MEM STAT
4 host02 onprem-clu 0 0 / 200 (0%) 0K / 3.8G (0%) on
3 host01 onprem-clu 0 0 / 200 (0%) 0K / 3.8G (0%) on
And similarly for the networks. You’ll have a public network and a network template to create as many private networks as you need:
$ onevnet list
ID USER GROUP NAME CLUSTERS BRIDGE STATE LEASES
4 oneadmin oneadmin onprem-cluster-public 102 onebr4 rdy 0
$ onevntemplate list
ID USER GROUP NAME REGTIME
0 oneadmin oneadmin onprem-cluster-private 04/28 18:08:38
For example let’s create a 192.168.0.100/26 network from the private network template:
onevntemplate instantiate 0 --ip 192.168.0.100 --size 64
VN ID: 5
Step 4. As a Simple test, Run a VM¶
As a simple test we’ll run a small VM, an Alpine Linux from the OpenNebula Public Marketplace.
onemarketapp list | grep -i alpine
74 Alpine Linux 3.20 6.10.0-2-2 256M rdy img 05/14/24 OpenNebula 0
51 Alpine Linux 3.17 6.10.0-2-2 256M rdy img 05/14/24 OpenNebula 0
40 Alpine Linux 3.16 6.10.0-2-2 256M rdy img 02/01/24 OpenNebula 0
27 Alpine Linux 3.19 6.10.0-2-2 256M rdy img 05/14/24 OpenNebula 0
22 Alpine Linux 3.18 6.10.0-2-2 256M rdy img 05/14/24 OpenNebula 0
We’ll select the newest version (ID 74 in this case) and add it to our cloud:
onemarketapp export 74 alpine_market -d default
IMAGE
ID: 2
VMTEMPLATE
ID: 3
The VM template has been created, with ID 3.
$ oneimage list
ID USER GROUP NAME DATASTORE SIZE TYPE PER STAT RVMS
3 oneadmin oneadmin alpine_market default 256M OS No rdy 0
The final step is adding a network interface to the template just created:
onetemplate update 3
...
NIC = [ NETWORK_MODE = "auto" ]
Now we can instantiate the VM from this template:
onetemplate instantiate 3
VM ID:11
The VM has been instantiated with ID 11. To see information for the VM:
onevm show 11
VIRTUAL MACHINE 10 INFORMATION
ID : 11
NAME : alpine_market-11
USER : oneadmin
GROUP : oneadmin
STATE : ACTIVE
LCM_STATE : RUNNING
...
VIRTUAL MACHINE MONITORING
CPU : 0.0
MEMORY : 173.7M
NETTX : 14K
NETRX : 54K
...
VM DISKS
ID DATASTORE TARGET IMAGE SIZE TYPE SAVE
0 default vda alpine_market 80M/256M file NO
1 - hda CONTEXT 1M/- - -
VM NICS
ID NETWORK BRIDGE IP MAC PCI_ID
0 onprem-cluster-publi onebr4 172.16.0.2 02:00:ac:10:00:02
You should now be able to connect to the VM via SSH:
$ ssh root@172.16.0.2
The authenticity of host '172.16.0.2 (172.16.0.2)' can't be established.
ED25519 key fingerprint is SHA256:Uz6WarB4k+1Sq2DI5Zz7b15p0ND7fr+kwxzIxSzr/Zg.
This key is not known by any other names
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
Warning: Permanently added '172.16.0.2' (ED25519) to the list of known hosts
localhost:~#
Operating Providers & Edge Clusters¶
Refer to the cluster operation guide to check all of the operations needed to create, manage, and delete an Edge Cluster. Refer to the providers guide to check all of the operations related to providers.
You can also manage On-premises Clusters using the OneProvision GUI in Sunstone.