AWS Edge Cluster¶
Edge Cluster Types¶
The AWS metal edge clusters uses baremetal instances to create OpenNebula Hosts, providing the best performance and highest capacity. These edge clusters can run LXC or KVM hypervisors.
AWS Edge Cluster Implementation¶
An Edge Cluster in AWS creates the following resources:
AWS instance: Host to run virtual machines.
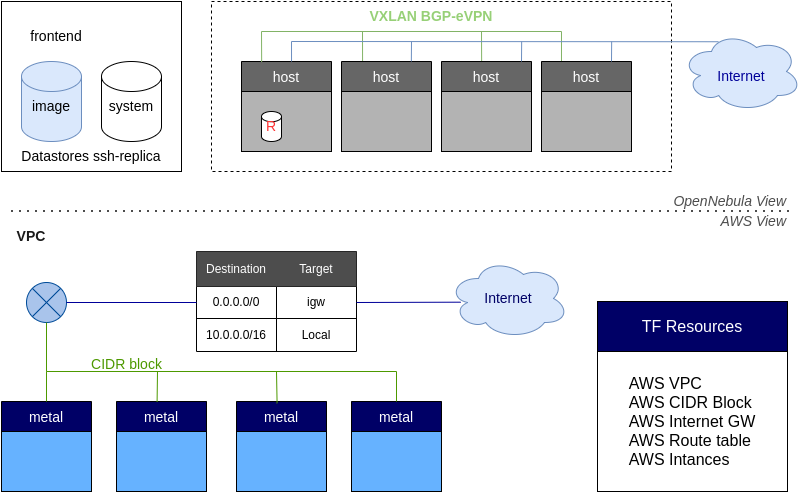
AWS VPC: it creates an isolated virtual network for all the deployed resources. There are some limits in the number of VPC that can be requested by the user, please refer to this link for more information.
AWS subnet: it allows communication between VMs that are running in the provisioned Hosts.
AWS internet gateway: it allows VMs to have public connectivity over Internet.
AWS security group: by default all the traffic is allowed, but custom security rules can be defined by the user to allow only specific traffic to the VMs.
The network model is implemented in the following way:
Public Networking: this is implemented using elastic IPs from AWS and the IPAM driver from OpenNebula. When the virtual network is created in OpenNebula, the elastic IPs are requested from AWS. Then, inside the Host, IP forwarding rules are applied so the VM can communicate over the public IP assigned by AWS. There are some limits to the number of elastic IPs that can be requested; please refer to this link for more information.
Private Networking: this is implemented using (BGP-EVPN) and VXLAN.
OpenNebula resources¶
The following resources, associated to each Edge Cluster, will be created in OpenNebula:
Cluster - containing all other resources
Hosts - for each AWS instance
Datastores - image and system datastores with SSH transfer manager using first instance as a replica
Virtual network - for public networking
Virtual network template - for private networking
Operating Providers & Edge Clusters¶
Refer to the cluster operation guide to check all the operations needed to create, manage, and delete an Edge Cluster. Refer to the providers guide to check all of the operations related to providers.
You can also manage AWS Clusters using the OneProvision GUI in Sunstone.
Virtual Provisions¶
All the above clusters make use of AWS metal instances. Virtual provisions are not enabled by default, to enable them execute the following command:
sudo ln -s /usr/share/one/oneprovision/edge-clusters-extra/virtual /usr/share/one/oneprovision/edge-clusters
# Edit /etc/one/fireedge/provision/providers.d/aws.yaml and uncomment virtual
Note that you only need to do this once for any virtual provider.