Clusters¶
Clusters group together Hosts, datastores and virtual networks that are configured to work together. A cluster is used to:
Ensure that VMs use resources that are compatible.
Assign resources to user groups by creating Virtual Private Clouds.
Clusters should contain homogeneous resources. Note that some operations like live migrations are restricted to Hosts in the same cluster.
The requirements for live migrating VMs between hosts of the same cluster are that no differences occur in the following areas of the hypervisors:
CPU model
Firmware settings
Microcode version
BIOS version
BIOS settings
Libvirt version
QEMU version
Kernel version
Cluster Management¶
Clusters are managed with the onecluster command. To create new clusters, use onecluster create <name>. Existing clusters can be inspected with the onecluster list and show commands.
onecluster list
ID NAME HOSTS NETS DATASTORES
onecluster create production
ID: 100
onecluster list
ID NAME HOSTS NETS DATASTORES
100 production 0 0 0
onecluster show production
CLUSTER 100 INFORMATION
ID : 100
NAME : production
HOSTS
VNETS
DATASTORES
Add Hosts to a Cluster¶
Every Host must belong to a cluster, so if no cluster is specified it will be assigned to the default cluster by default. Hosts can be created directly in a different cluster by using the --cluster option of onehost create, or be added at any time with the command onecluster addhost. Hosts can be in only one cluster at a time.
To delete a Host from a cluster, the command onecluster delhost must be used.
In the following example, we will add Host 0 to the cluster we created before. You will notice that the onecluster show command will list the Host ID 0 as part of the cluster.
onehost list
ID NAME CLUSTER RVM TCPU FCPU ACPU TMEM FMEM AMEM STAT
0 host01 - 7 400 290 400 3.7G 2.2G 3.7G on
onecluster addhost production host01
onehost list
ID NAME CLUSTER RVM TCPU FCPU ACPU TMEM FMEM AMEM STAT
0 host01 producti 7 400 290 400 3.7G 2.2G 3.7G on
onecluster show production
CLUSTER 100 INFORMATION
ID : 100
NAME : production
HOSTS
0
VNETS
DATASTORES
Add Resources to Clusters¶
Datastores and virtual networks can be added to multiple clusters. This means that any Host in those clusters is properly configured to run VMs using images from those datastores, or is using leases from those virtual networks.
For instance, if you have several Hosts configured to use a given Open vSwitch network, you would group them in the same cluster. The Scheduler will know that VMs using these resources can be deployed in any of the Hosts of the cluster.
These operations can be done with the onecluster addvnet/delvnet and adddatastore/deldatastore, respectively:
onecluster addvnet production priv-ovswitch
onecluster adddatastore production iscsi
onecluster list
ID NAME HOSTS NETS DATASTORES
100 production 1 1 1
onecluster show 100
CLUSTER 100 INFORMATION
ID : 100
NAME : production
CLUSTER TEMPLATE
HOSTS
0
VNETS
1
DATASTORES
100
The System Datastore for a Cluster¶
In order to create a complete environment where the scheduler can deploy VMs, your clusters need to have at least one System Datastore.
You can add the default System Datastore (ID: 0), or create a new one to improve its performance (e.g. balance VM I/O between different servers) or to use different System Datastore types (e.g. shared and ssh).
To use a specific System Datastore with your cluster, instead of the default one, just create it and associate it just like any other datastore (onecluster adddatastore).
Managing Clusters in Sunstone¶
The Sunstone UI interface offers an easy way to manage clusters and the resources within them. You will find the cluster sub-menu under the infrastructure menu. From there, you will be able to:
Create new clusters selecting the resources you want to include in this cluster.
See the list of current clusters, from which you can update the existing ones, or delete them.
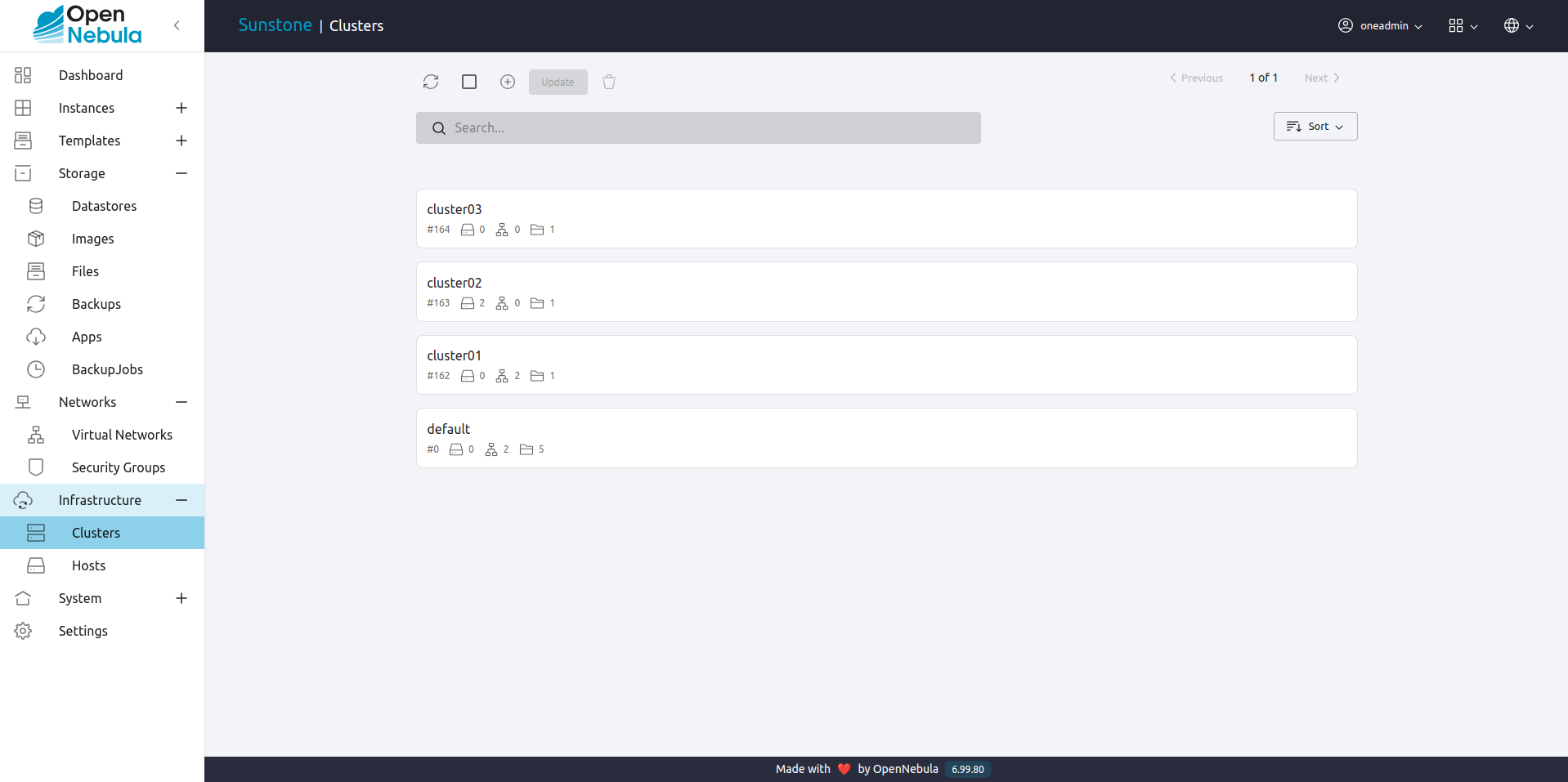
See cluster details and update overcommitment.