Backup Datastore: Rsync¶
RSync is an open source file transfer utility that is included with most distributions of Linux. This backup utility is provided with the Community Edition (CE) of OpenNebula and supports both full and incremental backup methods.
Step 0. Setup the backup server¶
First, a server should be configured to receive and store these backup files. The rsync backup server can be any server which is accessible from the oneadmin user on the hosts. This user on the nodes should have their key placed on the rsync server under the user specified in the rsync backup datastore configuration ( ~/.ssh/authorized_keys by default ).
Perform the following steps:
Create a user on the rsync server with permissions to access the datastore directory (default: /var/lib/one/datastores/<ds_id>)
Copy the public SSH keys from each node to the RSYNC_USER’s ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file on the RSYNC_HOST
Verify that the front-end and ALL hosts can SSH to the RSYNC_HOST as the RSYNC_USER without a password.
Create the folder /var/lib/one/datastores on the rsync server, and change ownership to the RSYNC_USER.
(Optional) Mount a storage volume to /var/lib/one/datastores, or to the Datastore ID directory under that.
Step 1. Create OpenNebula Datastore¶
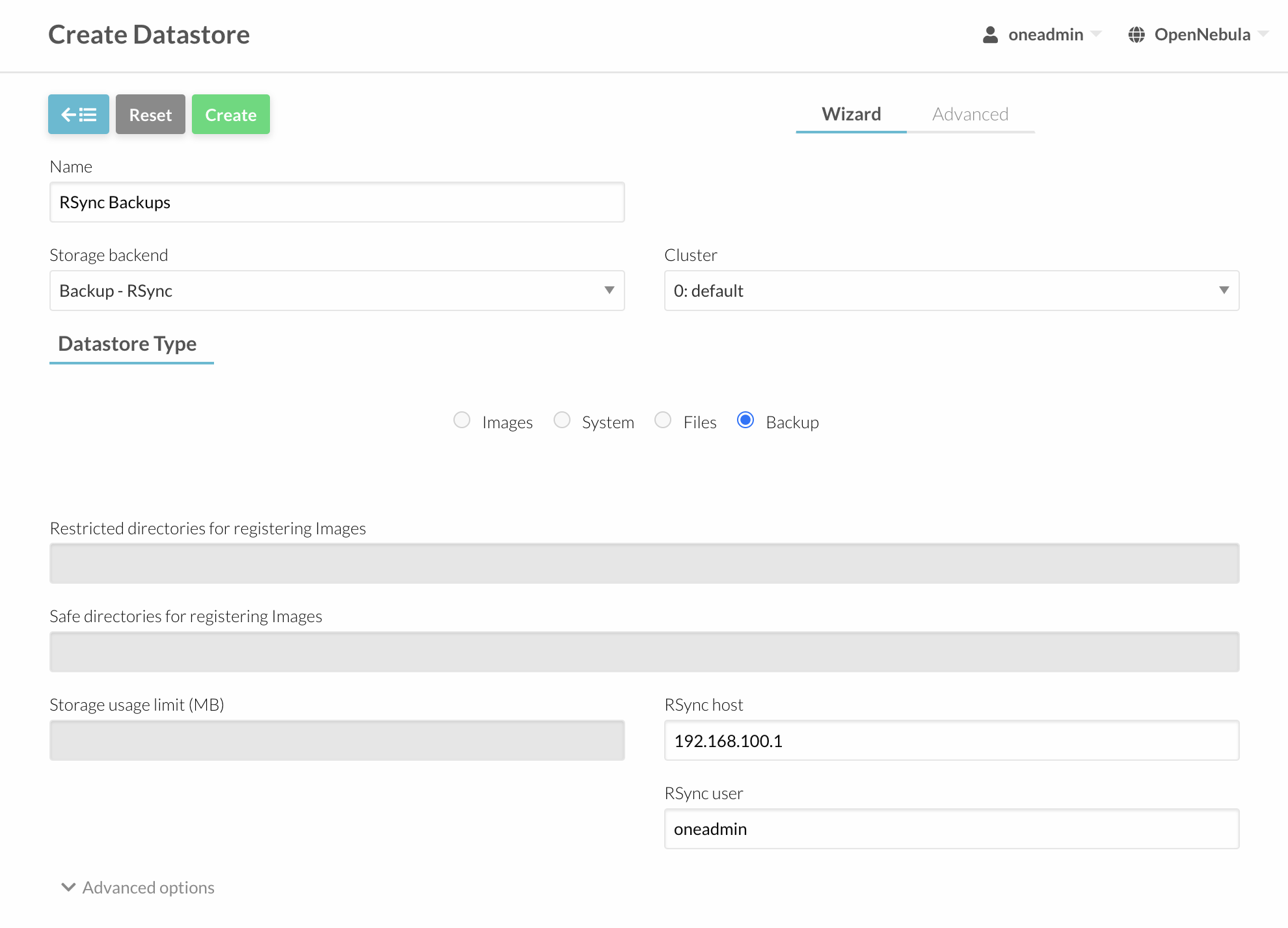
Once the rsync server is prepared to receive backup files from all of the nodes, we just need to create a datastore detailing the user and host:
cat ds_rsync.txt
NAME = "rsync Backups"
TYPE = "BACKUP_DS"
DS_MAD = "rsync"
TM_MAD = "-"
RSYNC_USER = "oneadmin"
RSYNC_HOST = "192.168.100.1"
Note: Transferring the backups over a separate network can improve performance and availability of the rest of the cloud.
With that file in place we just need to create the datastore from that:
onedatastore create ds_rsync.txt
ID: 100
Once these things are set up and it has been verified that all the hosts can access RSYNC_HOST using the RSYNC_USER, you should be able to start utilizing the rsync backup system. You can also create the DS through Sunstone like any other datastore:
Other Configurations¶
Limiting I/O and CPU usage¶
Backup operations may incur in a high I/O or CPU demands. This will add noise to the VMs running in the hypervisor. You can control resource usage of the backup operations by:
Lower the priority of the associated processes. Backup commands are run under a given ionice priority (best-effor, class 2 scheduler); and a given nice.
Confine the associated processes in a cgroup. OpenNebula will create a systemd slice for each backup datastore so the backup commands run with a limited number or read/write IOPS and CPU Quota.
Note that for the later, you need to delegate the cpu and io cgroup controllers to the oneadmin user. This way OpenNebula can set CPUQuota, IOReadIOPSMax and IOWriteIOPSMax.
To delegate the controllers you need to add the following file for oneadmin account (id 9869) in all the hosts (note that you’d probably need to create the user service folder):
cat /etc/systemd/system/user@9869.service.d/delegate.conf
[Service]
Delegate=cpu cpuset io
After that, reboot the hypervisor and double check that the setting is correct (you need to login as oneadmin):
cat /sys/fs/cgroup/user.slice/user-9869.slice/cgroup.controllers
cpuset cpu io memory pids
Temporary Backup Path¶
Disk images backups are generated within a local folder in the host where the VM is running. These images are later uploaded to the selected backup datastore. By default, this temporary path is set to the VM folder, in /var/lib/one/datastores/<DATASTORE_ID>/<VM_ID>/backup.
However, it’s possible to modify this path to utilize alternative locations, such as different local volumes, or to opt out of using the shared VM folder entirely.
To change the base folder to store disk backups for all hosts edit /var/lib/one/remotes/etc/datastore.conf and set the BACKUP_BASE_PATH variable. Please note this file uses shell syntax.
Reference: rsync Datastore Attributes¶
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
User to connect to the rsync server (Required) |
|
IP address of the backup server (Required) |
|
Command line arguments for rsync command (Default: -az) |
|
Temporary Directory used for rebasing incremental images (Default: /var/tmp) |
|
Run backups under a given ionice priority (best-effort, class 2). Value: 0 (high) - 7 (low) |
|
Run backups under a given nice. Value: -19 (high) to 19 (low) |
|
Run backups in a systemd slice, limiting the max number of read iops |
|
Run backups in a systemd slice, limiting the max number of write iops |
|
Run backups in a systemd slice with a given cpu quota (percentage). Use > 100 for using several CPUs |
|
Runs |