OneGate Configuration
The OneGate server allows Virtual Machines to pull and push information from/to OpenNebula. It can be used with both the KVM and LXC hypervisors if the guest operating system has preinstalled the OpenNebula contextualization package. It’s a dedicated daemon installed by default as part of the Single Front-end Installation, but can be deployed independently on a different machine. The server is distributed as an operating system package opennebula-gate with the system service opennebula-gate.
Read more in OneGate Usage.
Recommended Network Setup
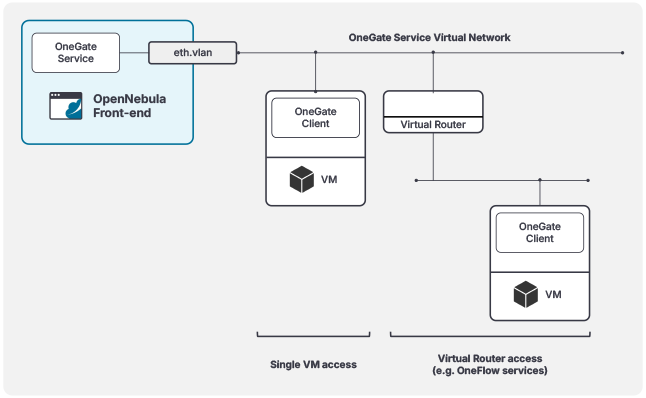
To use the OneGate Service, VMs must have connectivity to the service. We recommend setting up a dedicated Virtual Network, ideally on a separate VLAN, for OneGate access. To accomplish this, simply add a Virtual Network Interface (NIC) to the OneGate Service network for the VMs requiring access to the service. In cases where you’re deploying a multi-tier service, you can just add the virtual router to the OneGate Service network. The recommended network layout is illustrated in the diagram below:
Configuration
The OneGate configuration file can be found in /etc/one/onegate-server.conf on your Front-end. It uses YAML syntax, with the parameters listed in the table below.
 Note
Note
After a configuration change, the OneGate server must be restarted to take effect. Tip
Tip
For a quick view of any changes in configuration file options in maintenance releases, check the Resolved Issues page in the Release Notes for the release. Please note that even in the case of changes (such as a new option available), you do not need to update your configuration files unless you wish to change the application’s behavior.| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Server Configuration | |
:one_xmlrpc | Endpoint of OpenNebula XML-RPC API |
:host | Host/IP where OneGate will listen |
:port | Port where OneGate will listen |
:ssl_server | SSL proxy URL that serves the API (set if is being used) |
| Authentication | |
:auth | Authentication driver for incoming requests. * onegate based on tokens provided in VM context |
:core_auth | Authentication driver to communicate with OpenNebula core * cipher for symmetric cipher encryption of tokens* x509 for X.509 certificate encryption of tokensFor more information, visit the Cloud Server Authentication reference. |
| OneFlow Endpoint | |
:oneflow_server | Endpoint where the OneFlow server is listening |
| Permissions | |
:permissions | By default OneGate exposes all the available API calls. Each of the actions can be enabled/disabled in the server configuration. |
:restricted_attrs | Attributes that cannot be modified when updating a VM template |
:restricted_actions | Actions that cannot be performed on a VM |
:vnet_template_attributes | Attributes of the Virtual Network template that will be retrieved for Virtual Networks |
| Logging | |
:debug_level | Logging level. Values: 0 for ERROR level, 1 for WARNING level, 2 for INFO level, 3 for DEBUG level |
:expire_delta | Default interval for timestamps. Tokens will be generated using the same timestamp for this interval of time. THIS VALUE CANNOT BE LOWER THAN EXPIRE_MARGIN. |
:expire_margin | Tokens will be generated if time > EXPIRE_TIME - EXPIRE_MARGIN |
In the default configuration, the OneGate server will only listen to requests coming from localhost. Because the OneGate needs to be accessible remotely from the Virtual Machines, you need to change :host parameter in /etc/one/onegate-server.conf to a public IP of your Front-end Host or to 0.0.0.0 (to work on all IP addresses configured on Host).
Configure OpenNebula
Before Virtual Machines can communicate with OneGate, you need to edit /etc/one/oned.conf and set the OneGate endpoint in parameter ONEGATE_ENDPOINT. This endpoint (IP/hostname) must be reachable from the Virtual Machines over the network!
ONEGATE_ENDPOINT = "http://one.example.com:5030"
Restart the OpenNebula service to apply changes.
Service Control and Logs
Change the server running state by managing the operating system service opennebula-gate.
To start, restart, or stop the server, execute one of:
# systemctl start opennebula-gate
# systemctl restart opennebula-gate
# systemctl stop opennebula-gate
To enable or disable automatic start upon Host boot, execute one of:
# systemctl enable opennebula-gate
# systemctl disable opennebula-gate
Server logs are located in /var/log/one in the following files:
/var/log/one/onegate.log/var/log/one/onegate.error
Other logs are also available in Journald. Use the following command to show these:
# journalctl -u opennebula-gate.service
Advanced Setup
Example: Use Transparent OneGate Proxy to Improve Security
Add the following config snippet to the ~oneadmin/remotes/etc/vnm/OpenNebulaNetwork.conf file on Front-end machines:
:tproxy:
# OneGate service.
- :service_port: 5030
:remote_addr: 10.11.12.13 # OpenNebula Front-end VIP
:remote_port: 5030
Propagate config to hypervisor Hosts, execute as oneadmin on the leader Front-end machine:
$ onehost sync -f
Deploy a guest Virtual Machine and test OneGate connectivity from within:
$ onegate vm show
Read more in Transparent Proxies.
We value your feedback
Was this information helpful?
Glad to hear it
Sorry to hear that