Usage Quotas
The quota system tracks user and group usage of system resources, and allows the system administrator to set limits on the usage of these resources. Quota limits can be set for:
- users, to individually limit the usage by a given user.
- groups, to limit the overall usage by all the users in a given group. This can be of special interest for the OpenNebula Zones and Virtual Data Center (VDC) components.
Resource Limits
The quota system allows you to track and limit usage on:
- Datastores, to control the amount of storage capacity allocated to each user/group for each datastore.
- Compute, to limit the overall memory, CPU, or VM instances.
- Network, to limit the number of IPs a user/group can obtain from a given network. This is especially interesting for networks with public IPs, which are usually a limited resource.
- Images, you can limit how many VM instances from a given user/group are using a given image. You can take advantage of this quota when the image contains consumable resources (e.g., software licenses).
Defining User/Group Quotas
Usage quotas are set in the OpenNebula template syntax (either plain text or XML). The following tables summarize the attributes to define a quota for each resource type.
Datastore Quotas
The attribute name is DATASTORE.
| DATASTORE Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
ID | ID of the datastore to set the quota for |
SIZE | Maximum size in MB that can be used in the datastore. It includes size of images and their snapshots. |
IMAGES | Maximum number of images that can be created in the datastore |
Compute Quotas
The attribute name is VM.
| VM Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
CLUSTER_IDS | An optional attribute used to define which clusters are included in this quota. Leave this attribute empty to apply the quota globally. |
VMS | Maximum number of VMs that can be created |
MEMORY | Maximum memory in MB that can be requested by user/group VMs |
CPU | Maximum CPU capacity that can be requested by user/group VMs |
RUNNING VMS | Maximum number of VMs that can be running |
RUNNING MEMORY | Maximum memory in MB that can be running by user/group VMs |
RUNNING CPU | Maximum CPU capacity that can be running by user/group VMs |
SYSTEM_DISK_SIZE | Maximum size (in MB) of system disks that can be requested by user/group VMs. It includes size of volatile and non-persistent disks (including disk snapshots) and VM snapshots (reduced by VM_SNAPSHOT_FACTOR). |
The actual size given on the system and image datastores depends on the storage driver used. The behavior of the driver is described by the CLONE_TARGET and LN_TARGET attributes, see Transfer Driver configuration
 Important
Important
Running quotas will be increased or decreased depending on the state of the Virtual Machine. The states in which the machine is counted as “Running” are ACTIVE , HOLD, PENDING, and CLONING.Generic Quotas
Administrators have the capability to expand Compute Quotas by introducing the QUOTA_VM_ATTRIBUTE into the OpenNebula configuration file. This attribute allows any numerical attribute from the Virtual Machine Template or User Template to serve as a generic quota.
As an example, one could categorize each VM template into a specific Quality of Service (QoS) category based on attributes like CPU and append a metric to denote this:
CPU = 12
MEMORY = 4096
...
GOLD_QOS = 1
Subsequently, a quota can be enforced for a user, e.g., GOLD_QOS = 5, meaning that the user is restricted to a maximum of 5 VMs within the GOLD_QOS category. Administrators have the flexibility to determine which VMs fall under a category by utilizing any combination of VM attributes. Similarly, limitations can be set on the number of PCI passthrough GPUs by adding GPU = 1 to templates incorporating such devices…
Each generic quota is also automatically prefixed with RUNNING_. For instance, RUNNING_GOLD_QOS would specify the number of VMs in an ACTIVE state with the GOLD_QOS attribute. This allows you to define quotas specifically tailored for running VMs.
Additionally, it’s important to note that each generic quota defined with the QUOTA_VM_ATTRIBUTE is automatically included in the VM_RESTRICTED_ATTR set. This inclusion prevents regular users from circumventing the quota system by altering the attributes related to these generic quotas.
Per Cluster Quotas
For more granular control over Compute Quotas, use the CLUSTER_IDS attribute. This optional attribute specifies which clusters the quota applies to. If left empty, the quota will be applied globally. The value should be a comma-separated list of cluster IDs, and the quota will only affect VMs running in the specified clusters. Note that each cluster can be assigned to only one quota.
# Global quota to allow 4 VMs
VM = [
VMS = 4
]
# Quota for cluster 0 to allow 2 VMs
VM = [
CLUSTER_IDS = "0",
VMS = 2
]
# Quota for clusters 100 and 101 to allow 3 VMs
VM = [
CLUSTER_IDS = "100,101",
VMS = 3
]
In this setup, the user can run:
- Up to 2 VMs in cluster 0
- Up to 3 VMs in clusters 100 and 101 combined
- No more than 4 VMs in total across all clusters
Network Quotas
The attribute name is NETWORK.
| NETWORK Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
ID | ID of the Network to set the quota for |
LEASES | Maximum IPs that can be leased from the Network |
Image Quotas
The attribute name is IMAGE.
| IMAGE Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
ID | ID of the Image to set the quota for |
RVMS | Maximum VMs that can use this Image at the same time |
Quota Limits and Usage
For each quota there are two special limits:
- -1 means that the default quota will be used
- -2 means unlimited
 Warning
Warning
Each quota has an associated usage counter named <QUOTA_NAME>_USED. For example MEMORY_USED means the total memory used by user/group VMs, and its associated quota is MEMORY.The following template shows a quota example for a user in plain text. The template limits the overall usage in Datastore 0 to 20Gb (for an unlimited number of images); the number of VMs that can be created to 4, with a maximum memory of 2G and 5 CPUs; and the number of leases on network 1 to 4. Additionally, Image 1 can only be used by 3 VMs at the same time.
DATASTORE=[
ID="1",
IMAGES="-2",
SIZE="20480"
]
VM=[
CPU="5",
MEMORY="2048",
VMS="4",
SYSTEM_DISK_SIZE="-1"
]
NETWORK=[
ID="1",
LEASES="4"
]
IMAGE=[
ID="1",
RVMS="3"
]
IMAGE=[
ID="2",
RVMS="-2"
]
 Warning
Warning
Note that whenever a network, image, datastore, or VM is used, the corresponding quota counters are created for the user with an unlimited value. This allows the tracking of each user/group’s usage even when quotas are not used.Setting User/Group Quotas
User/group quotas can be easily set up either through the command line interface or Sunstone. Note that you need MANAGE permissions to set a quota of a user and ADMIN permissions to set the quota of a group. In this way, by default, only oneadmin can set quotas for a group, but if you define a group manager, this manager can set specific usage quotas for the users on their group (thus distributing resources as required). You can always change this behavior by setting the appropriate ACL rules.
To set the quota for a user, e.g., userA, just type:
$ oneuser quota userA
This will open an editor session to edit a quota template (with some tips about the syntax).
 Warning
Warning
Usage metrics are included for information purposes (e.g., CPU_USED, MEMORY_USED, LEASES_USED…) you cannot modify them Warning
Warning
You can add as many resource quotas as needed even if they have not been automatically initialized.Similarly, you can set the quotas for group A with:
$ onegroup quota groupA
The batchquota command allows you to set the same quotas for several users or groups:
$ oneuser batchquota userA,userB,35
$ onegroup batchquota 100..104
Setting Default Quotas
There are two default templates for quota limits, one for users and another for groups. This template applies to all users/groups unless they have an individual limit set.
Use the oneuser/onegroup defaultquota command:
$ oneuser defaultquota
By default, the quota is set to unlimited. Once the editor opens after issuing oneuser defaultquota you’ll see comments regarding how to set the quotas and no quota template. Setting a quota with a template using unlimited values will translate to a blank quota. If you issue oneuser defaultquota again, you’ll see the same comments with blank quota. If you set a non-unlimited quota, you’ll see the value of the quota that is established as default.
Default Quotas don’t apply for Cluster Quotas, you need to set them manually.
Checking User/Group Quotas
Quota limits and usage for each user/group are included as part of the standard information, so they can be easily checked with the usual commands. See for example:
$ oneuser show uA
USER 2 INFORMATION
ID : 2
NAME : uA
GROUP : gA
PASSWORD : a9993e364706816aba3e25717850c26c9cd0d89d
AUTH_DRIVER : core
ENABLED : Yes
USER TEMPLATE
VMS USAGE & QUOTAS
CLUSTERS VMS MEMORY CPU SYSTEM_DISK_SIZE
1 / 4 1M / - 2.00 / - 0M / -
100 0 / 0M / 128G 0.00 / 10.00 0M / -
VMS USAGE & QUOTAS - RUNNING
CLUSTERS RUNNING VMS RUNNING MEMORY RUNNING CPU
1 / - 1M / - 2.00 / -
100 0 / 2 0M / 128G 0.00 / -
DATASTORE USAGE & QUOTAS
NETWORK USAGE & QUOTAS
IMAGE USAGE & QUOTAS
And for the group:
$ onegroup show gA
GROUP 100 INFORMATION
ID : 100
NAME : gA
USERS
ID
2
3
VMS USAGE & QUOTAS
VMS MEMORY CPU SYSTEM_DISK_SIZE
1 / 4 1M / - 2.00 / - 0M / -
VMS USAGE & QUOTAS - RUNNING
RUNNING VMS RUNNING MEMORY RUNNING CPU
1 / - 1M / 2M 2.00 / -
DATASTORE USAGE & QUOTAS
NETWORK USAGE & QUOTAS
IMAGE USAGE & QUOTAS
Managing Quotas with Sunstone
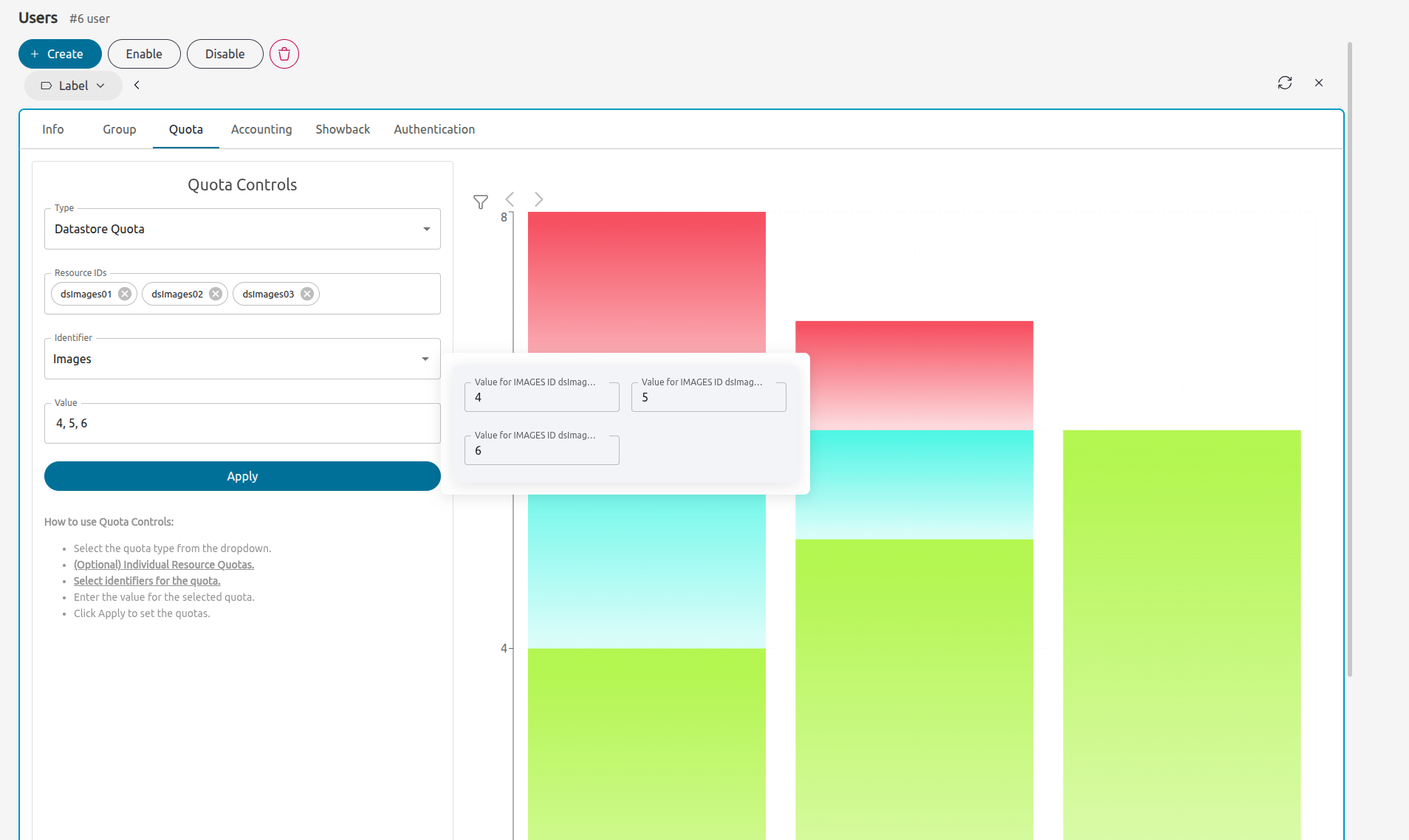
You can easily set the user/group quotas in Sunstone through the user/group tab. Similarly, usage and quota information is also available as part of the user/group information:
We value your feedback
Was this information helpful?
Glad to hear it
Sorry to hear that