Using FireEdge Sunstone¶
Overview¶
FireEdge Sunstone is the new generation OpenNebula web interface, fully featured for VM and VM Template management and with other sections ready covering most functionality for end users.
This interface is delivered by the FireEdge server, and it is its main interface, meaning that it will redirect to Sunstone when contacted in the http://<OPENNEBULA-FRONTEND>:2616/ address.
Warning
FireEdge Sunstone is fully functional for VM and VM Template management, but it lacks all the functionality of the traditional Ruby Sunstone. FireEdge Sunstone is still in BETA stage.
Configuration¶
To configure FireEdge Sunstone, there are several options to consider, and they are described in the FireEdge Configuration guide.
Usage¶
This completely fresh user experience is available by accessing http://<OPENNEBULA-FRONTEND>:2616. On the left menu, the users can find the available tabs to manage resources, as described in the Sections part of this guide.
Sunstone users can change their current view from the top-right dropdown menu:
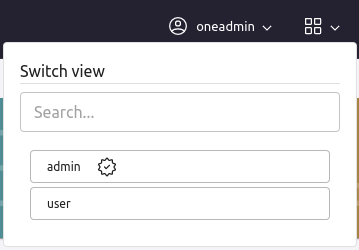
They can also configure several options from the settings tab.
Sections¶
The available FireEdge Sunstone sections and their tabs are described in the following subsections. All the tabs described below can be deactivated in the FireEdge Sunstone views
Instances¶
VMs Tab: Users can see all their Virtual Machines, and perform managing actions such as changing permissions, attaching disks, attaching networks, taking snapshots, adding scheduled actions, remote console connections, and more. From this tab, users can also instantiate a new Virtual Machine. Some VM actions can be through multiple VMs, such as:
suspend,stop,power-off,reboot,resume,undeployand more.
Templates¶
VM Template Tab: Users can see all their Templates, and perform updates and clones. From this tab, user can also instantiate a Virtual Machine. Also, the user can perform some managing operations over the templates, such as: change permissions, share and unshare, lock and unlock, and more.
Storage¶
Datastores Tab: Users can see all their
FILE,IMAGE, andSYSTEMdatastores. Also, the users can perform some managing actions, such as changing permissions, enabling and disabling, and more. From this tab, users can create a new Datastore of one of the types described before.Images Tab: Users can see all their
OS,CDROM, andDATABLOCKimages. Also, the users can perform some managing actions, such as changing permissions, locking and unlocking, and more. From this tab, users can instantiate a new Image of one of the types described before.Files Tab: Users can see all their
KERNEL,RAMDISK, andCONTEXTimages. Also, the users can perform some managing actions, such as changing permissions, enabling and disabling, and more. From this tab, users can instantiate a new Image of one of the types described before.Backups Tab: Users can see all their
BACKUPimages. Also, the users can perform some managing actions, such as changing permissions and restoring.Marketplace Apps Tab: Users can see all the apps from their active marketplaces, download and create templates from them, or download them locally on their computers.
Networks¶
Virtual Networks Tab: Users can see all their Virtual Networks, and perform managing operations such as updating, reserving, changing permissions, and more. Also, users can create a new Virtual Network from this tab.
Security Groups Tab: Users can see all their Security Groups, and perform managing operations such as updating, cloning, committing, changing permissions, and more. Also, users can create a new Security Group from this tab.
Infrastructure¶
Clusters Tab: Users can see all their Clusters.
Hosts Tab: Users can see all their Hosts, and perform managing operations such as enabling, disabling, and more. Also, users can create a new Host from this tab.
System¶
VDCs Tab: Users can see all their VDCs, and can update, rename and view the resources associated with them, and more. Also, users can create a new VDC from this tab.
Users Tab: Admins can access all the users defined in the OpenNebula instance, and perform managing operations such as updating, enabling/disabling, setting quotas, and more. Also, admins can create new Users from this tab.
Settings¶
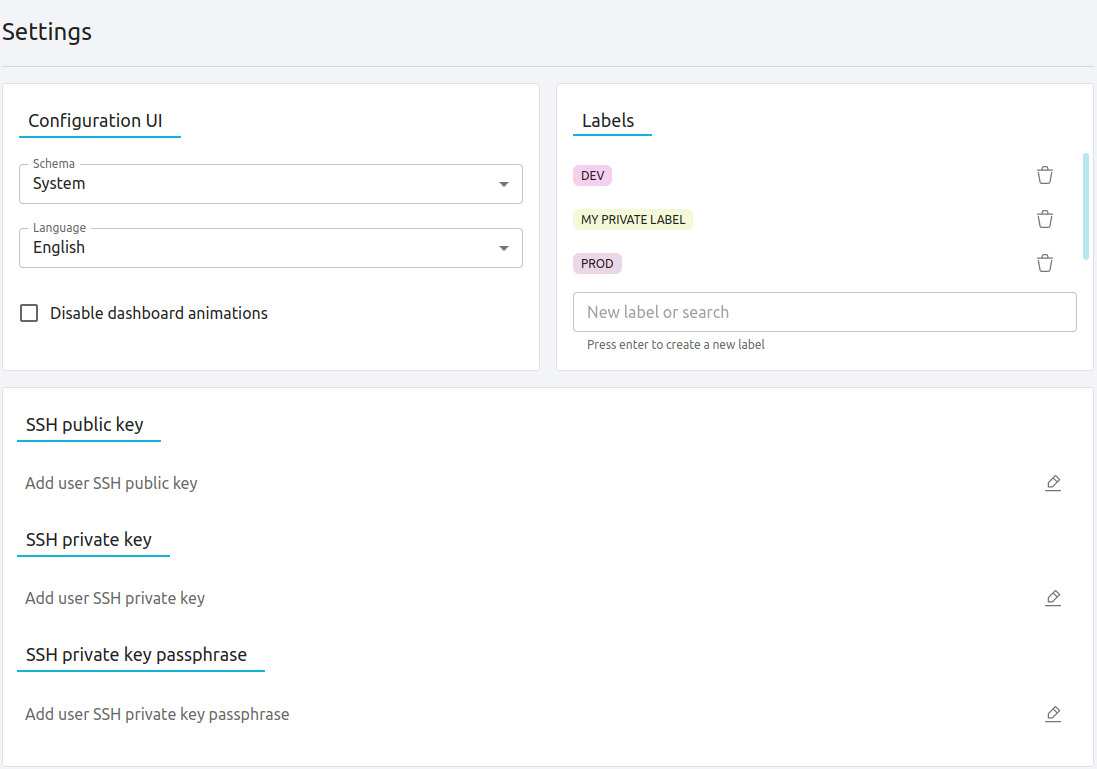
From this section, users can define multiple configuration options for themselves, that willl be saved inside the user template, such as:
Schema (default = System): change the FireEdge Sunstone Theme to dark, light or matching with the system.
Language (default = English US): select the language that they want to use for the UI.
Disable the dashboard animations. By default they are enabled.
Labels: allows the user to manage their labels.
SSH Public key: allows the user to specify a public SSH key that they can use on the VMs.
SSH Private key: allows the user to specify a private SSH key that they can use when establishing connections with their VMs.
SSH Private key passphrase: if the private SSH key is encrypted, the user must specify the password.
Note
All the configurations set in this section will be in the user template.
Views¶
Using the FireEdge Sunstone views, you can provide a simplified UI aimed at end-users of an OpenNebula cloud. FireEdge Sunstone Views are fully customizable, so you can easily enable or disable specific information tabs or action buttons. You can define multiple views for different user groups. Each view defines a set of UI components, so each user accesses and views the relevant parts of the cloud for their role. Default views:
Each view is in an individual directory, admin and user that OpenNebula proposes by default, as described in the next section.
Default Views¶
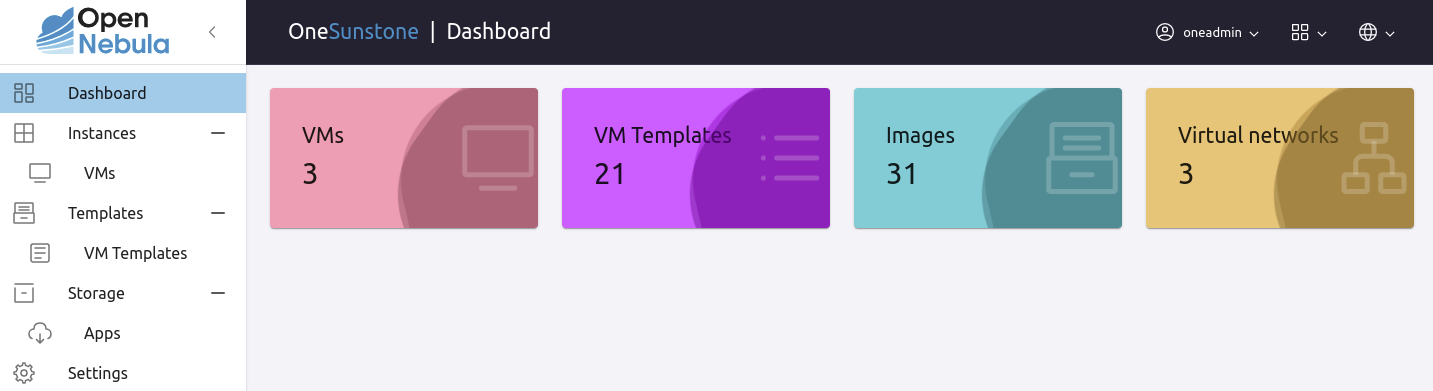
Admin View¶
This view provides complete control of the Virtual Machines, Templates, and Marketplace apps. Details can be configured in the /etc/one/fireedge/sunstone/admin/ directory.
User View¶
Based on the Admin View. It is an advanced user view intended for users with fewer privileges than an admin user, allowing them to manage Virtual Machines and Templates. Users will not be able to manage or retrieve the hosts and clusters of the cloud. Details can be configured in the /etc/one/fireedge/sunstone/user/ directory.
Defining a New View¶
The views definitions are placed in the /etc/one/fireedge/sunstone/ directory. Each view is defined by a folder (named as the view) with the needed configuration files inside.
/etc/one/fireedge/sunstone/
...
|-- admin/
| |-- backup-tab.yaml <--- the Backup tab configuration file
| |-- cluster-tab.yaml <--- the Cluster tab configuration file (not installed by default)
| |-- datastore-tab.yaml <--- the Datastore tab configuration file
| |-- file-tab.yaml <--- the File tab configuration file
| |-- host-tab.yaml <--- the Host tab configuration file
| |-- image-tab.yaml <--- the Image tab configuration file
| |-- marketplace-app-tab.yaml <--- the Marketplace App tab configuration file
| |-- sec-group-tab.yaml <--- the Security Group tab configuration file
| |-- user-tab.yaml <--- the User tab configuration file
| |-- vdc-tab.yaml <--- the VDC tab configuration file
| |-- vm-tab.yaml <--- the VM tab configuration file
| |-- vm-template-tab.yaml <--- the VM Template tab configuration file
| |-- vnet-tab.yaml <--- the Virtual Network tab configuration file
|-- sunstone-server.conf
|-- sunstone-views.yaml <--- the FireEdge Sunstone views main configuration
`-- user/
...
|-- vm-tab.yaml <--- the VM tab configuration file
`-- vm-template-tab.yaml <--- the VM Template tab configuration file
...
The easiest way to create a custom view is to copy the admin or user folder and modify its content as needed. After that, add the new view into /etc/one/fireedge/sunstone/sunstone-views.yaml.
View Customization¶
On FireEdge Sunstone each view is defined by a folder that has the YAML files for the configured tabs. The content for those files is divided into sections that are described in the following sections.
In the following tables, the description field contains the expected behavior when is set to true.
Note
The attributes can be modified only if they come in the YAML file by default. If an attribute is not present, it has the same behavior as when it is set to false.
Actions¶
The attributes described here indicate which buttons are visible to operate over the resources. The following attributes must be nested in an actions tag.
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Users will be able to create a Virtual Machine backup. |
|
Users will be able to change the resource cluster. |
|
Users will be able to change the resource group. |
|
Users will be able to change the resource owner. |
|
Users will be able to clone the resource. |
|
Users will be able to commit the security group changes. |
|
Users will be able to create a new marketplace app from the resource. |
|
Users will be able to create a new resource. |
|
Users will be able to delete the resource. |
|
Users will be able to manually deploy Virtual Machines. |
|
Users will be able to disable the resource. |
|
Users will be able to create an image from dockerfile. |
|
Users will be able to download apps from the marketplace into their computers. |
|
Users will be able to edit the resource labels. |
|
Users will be able to enable the resource. |
|
Users will be able to export apps from the marketplace into a datastore. |
|
Users will be able to set to hold Virtual Machines. |
|
Users will be able to instantiate the resouce. |
|
Users will be able to lock the resource. |
|
Users will be able to migrate a Virtual Machine to a different host and datastore. |
|
Users will be able to live migrate a Virtual Machine to a different host and datastore. |
|
Users will be able to migrate a Virtual Machine in poweroff to a different host and datastore. |
|
Users will be able to migrate a Virtual Machine in poweroff (hard way) to a different host and datastore. |
|
Users will be able to set an image as non-persistent. |
|
Users will be able to set a host as offline. |
|
Users will be able to set an image as persistent. |
|
Users will be able to poweroff Virtual Machines. |
|
Users will be able to poweroff Virtual Machines (hard way). |
|
Users will be able to establish an RDP connection. |
|
Users will be able to reboot Virtual Machines. |
|
Users will be able to reboot Virtual Machines (hard way). |
|
Users will be able to recover Virtual Machines. |
|
Users will be able to release Virtual Machines. |
|
Users will be able to reschedule Virtual Machines. |
|
Users will be able to reserve addresses from a Virtual Network. |
|
Users will be able to restore a backup image. |
|
Users will be able to resume Virtual Machines. |
|
Users will be able to save a Virtual Machine as a VM Template. |
|
Users will be able to share VM Templates. |
|
Users will be able to establish a SSH connection. |
|
Users will be able to stop Virtual Machines. |
|
Users will be able to suspend Virtual Machines. |
|
Users will be able to terminate Virtual Machines. |
|
Users will be able to terminate Virtual Machines (hard way). |
|
Users will be able to undeploy Virtual Machines. |
|
Users will be able to undeploy Virtual Machines (hard way). |
|
Users will be able to unlock the resource. |
|
Users will be able to update the resource. |
|
Users will be able to un-reschedule Virtual Machines. |
|
Users will be able to unshare VM Templates. |
|
Users will be able to establish a VMRC connection. |
|
Users will be able to establish a VNC connection. |
Filters¶
The attributes described here indicate which filters are visible to select resources. The following attributes must be nested in a filters tag.
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Filtering by the resource group will be enabled. |
|
Filtering by the resource hostname will be enabled. |
|
Filtering by the resource IPs will be enabled. |
|
Filtering by the resource labels will be enabled. |
|
Filtering by the resource lock state will be enabled. |
|
Filtering by the marketplace will be enabled. |
|
Filtering by the resource owner will be enabled. |
|
Filtering by the resource state will be enabled. |
|
Filtering by the resource type will be enabled. |
|
Filtering by the Virtual Network driver will be enabled. |
|
Filtering based on if the resource is for vRouters will be enabled. |
|
Filtering by the resource zone will be enabled. |
Info Tabs¶
The attributes described here indicate the available actions on each info tab on the resource. The following attributes must be nested in an info-tabs and the corresponding tab.
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Describes a list of available actions on this tab that can be disabled. |
|
Describes the behavior for the |
|
Describes the behavior for the |
|
This tab will be showed in the resource info. |
|
Describes the behavior for the |
|
Describes the behavior for the |
|
Describes the behavior for the |
|
Describes the behavior for the |
|
Describes the behavior for the |
|
Describes the behavior for the |
|
Describes the behavior for the |
|
Describes the behavior for the |
|
Describes the behavior for the |
The available actions in the info tabs are described in the following table.
Action |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Users will be able to add information to that panel. |
|
Users will be able to add an address range. |
|
Users will be able to add a security group. |
|
Users will be able to attach disks. |
|
Users will be able to attach NICs. |
|
Users will be able to attach security groups to NICs. |
|
Users will be able to create charters. |
|
Users will be able to change the resource group. |
|
Users will be able to change the resource permissions. |
|
Users will be able to change the resource owner. |
|
Users will be able to copy the information available in that panel. |
|
Users will be able to delete the information available in that panel. |
|
Users will be able to delete an address range. |
|
Users will be able to delete a security group. |
|
Users will be able to detach disks. |
|
Users will be able to detach NICs. |
|
Users will be able to detach security groups to NICs. |
|
Users will be able to save disks as an image. |
|
Users will be able to edit the information available in that panel. |
|
Users will be able to hold a lease. |
|
Users will be able to release a lease. |
|
Users will be able to rename the resource. |
|
Users will be able to perform capacity resize. |
|
Users will be able to perform disk resize. |
|
Users will be able to create scheduled actions. |
|
Users will be able to delete scheduled actions. |
|
Users will be able to update scheduled actions. |
|
Users will be able to create snapshots. |
|
Users will be able to delete snapshots. |
|
Users will be able to create disk snapshots. |
|
Users will be able to delete disk snapshots. |
|
Users will be able to rename disk snapshots. |
|
Users will be able to revert disk snapshots. |
|
Users will be able to revert snapshots. |
|
Users will be able to update an address range. |
|
Users will be able to update the configurations. |
|
Users will be able to update the NICs. |
Features¶
The attributes described here indicate which features are used for the resources. The following attributes must be nested in a features tag.
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Users won’t be able to change the CPU settings. |
|
Users won’t be able to scale the CPU. |
Dialogs¶
The attributes described here indicate the available actions on each dialog on the resource.
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Backup section will be displayed. |
|
Booting section will be displayed. |
|
Capacity section will be displayed. |
|
Context section will be displayed. |
|
Information section will be displayed. |
|
Input/Output section will be displayed. |
|
Network section will be displayed. |
|
Numa section will be displayed. |
|
Ownership section will be displayed. |
|
Placement section will be displayed. |
|
Scheduled Actions section will be displayed. |
|
Showback section will be displayed. |
|
Storage section will be displayed. |
|
vCenter section will be displayed. |
|
VM groups section will be displayed. |
Remote connections¶
OpenNebula VNC remote connection.¶
Sunstone allows direct connections to VMs using VNC. It admits parameters such as configuring the host and port for remote connections, configuring the keyboard layout (needed for qemu KVM hosts), and setting a connection password.
To set these VNC connection configurations, we must:
Go to the VM template configuration and click on create or update an existing one.
Go to the “Advanced options” step and click on Input/Output.
Under the “Graphics” section, you can see all the VNC configurations.
Note
To have the correct layout on your Virtual Machine, you must set the same keymap inside the Virtual Machine as the KEYMAP attribute configured in the OpenNebula VM graphics section, and it must be the same as your keyboard layout.
OpenNebula RDP remote connection.¶
Sunstone also admits direct connections using RDP. This kind of connection is bound to a network interface, meaning that to enable it, you must follow the following steps:
Go to the VM template tab and click on create or update an existing one.
Go to the “Advanced options” step.
Click on “Network”.
Click on attach nic or update an existing one.
Go to the “Advanced options” step, and enable the RDP connection and all the desired configuration parameters for the connection.
Note
To enable them on a running VM, you must follow steps 3 to 5 once you click the VM you want to have it.
OpenNebula SSH remote connection.¶
Sunstone also allows direct connections using SSH. This kind of connection is bound to a network interface, meaning that to enable it, you must follow the following steps:
Go to the VM template tab and click on create or update an existing one.
Go to the “Advanced options” step.
Click on “Network”.
Click on attach nic or update an existing one.
Go to the “Advanced options” step, and enable the SSH connection.
Note
To enable them on a running VM, you must follow steps 3 to 5 once you click the VM you want to have it.