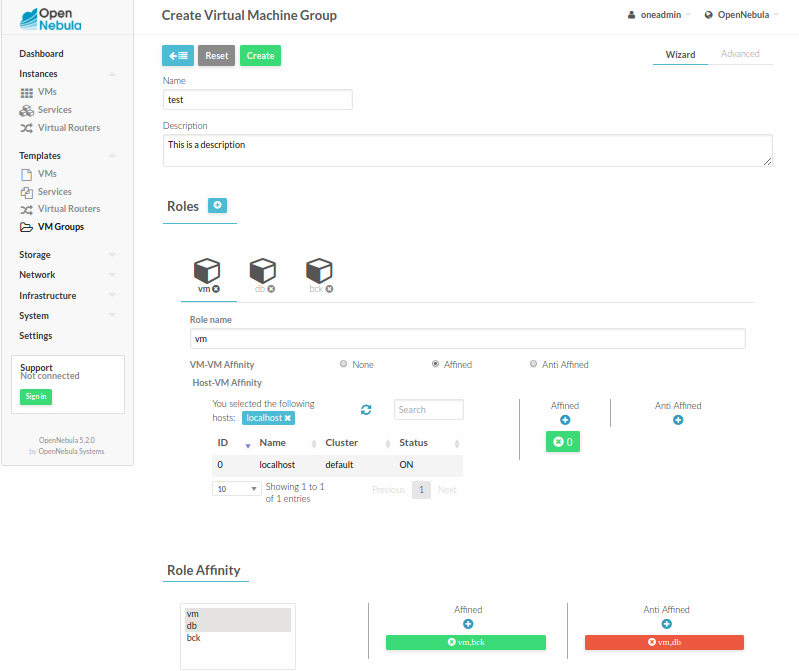
Virtual Machine Affinity¶
A VM Group defines a set of related VMs, and associated placement constraints for the VMs in the group. A VM Group allows you to place together (or separately) certain VMs (or VM classes, called roles). VMGroups will help you to optimize the performance (e.g. not placing all the CPU bound VMs in the same host) or improve the fault tolerance (e.g. not placing all your front-ends in the same host) of your multi-VM applications.
Defining a VM Group¶
A VM Group consists of two parts: a set of roles, and a set of placement constraints for the roles. In a VM Group, a role defines a class of virtual machines that are subject to the same placement constraints and rules. Usually, you will put in the same role VMs implementing a given functionality of a multi-VM application, e.g. the front-ends or the database VMs. Additionally, you can define placement constraints for the VMs in the VM-Group, this placement rules can refer to the VMs within a role or VMs across roles.
A role is defined with the following attributes:
Attribute |
Mandatory |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
YES |
The name of the role, it needs to be unique within the VM Group . |
|
NO |
Placement policy for the VMs of the role. Possible values are: |
|
NO |
Defines a set of hosts (by their ID) where the VMs of the role can be executed. |
|
NO |
Defines a set of hosts (by their ID) where the VMs of the role cannot be executed. |
Additional placement constraints can be imposed to the VMs of a role with the following attributes:
Attribute |
Mandatory |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
NO |
List of roles (comma separated) whose VMs has to be placed in the same host. |
|
NO |
List of roles (comma separated) whose VMs cannot be placed in the same host. |
To create a VM Group, use the Sunstone web interface, or create a template file following this example:
cat ./vmg.txt
NAME = "multi-tier server"
ROLE = [
NAME = "front-end",
POLICY = "ANTI_AFFINED"
]
ROLE = [
NAME = "apps",
HOST_AFFINED = "2,3,4"
]
ROLE = [ NAME = "db" ]
AFFINED = "db, apps"
onevmgroup create ./vmg.txt
ID: 0
Placement Policies¶
The following placement policies cane be applied to the VMs of a VM Group.
VM to Host Affinity¶
Specifies a set of hosts where the VMs of a role can be allocated. This policy is set in a role basis using the HOST_AFFINED and HOST_ANTI_AFFINED attributes. The host affinity rules are compatible with any other rules applied to the role VMs.
For example, if you want to place the VMs implementing the database for your application in high performance hosts you could use:
ROLE = [
NAME = "database",
HOST_AFFINED = "1,2,3,4"
]
VM to VM Affinity¶
Specifies whether the VMs of a role have to be placed together in the same host (AFFINED) or scattered across different hosts (ANTI_AFFINED). The VM to VM affinity is set per role with the POLICY attribute.
For example, you may want to spread CPU-bound VMs across hosts to prevent contention
ROLE = [
NAME = "workers",
POLICY = "ANTI_AFFINED"
]
Role to Role Affinity¶
Specifies whether the VMs of a role have to be placed together or separately with the VMs of other role. This useful to combine the Host-VM and VM-VM policies. Affinity rules for roles are set with the AFFINED and ANTI_AFFINED attributes.
For example, consider that you need the VMs of a database to run together so they access the same storage. At the same time, you need all the backup VMs to run in a separate hosts; and you need database and backups to be also in different hosts. Finally, you may have some constraints about where the database and backups may run:
ROLE = [
NAME = "databases",
HOST_AFFINED = "1,2,3,4,5,6,7"
POLICY = "AFFINED"
]
ROLE = [
NAME = "backup",
HOST_ANTI_AFFINED = "3,4"
POLICY = "ANTI_AFFINED"
]
ANTI_AFFINED = "databases, backup"
Important
Note that a role policy has to be coherent with any role-role policy, i.e. a role with an ANTI_AFFINED policy cannot be included in any AFFINED role-role rule.
Scheduler Configuration and Remarks¶
VMGroups are placed by dynamically generating the requirement (SCHED_REQUIREMENTS) of each VM an re-evaluating these expressions. Moreover, the following is also considered:
The scheduler will look for a host with enough capacity for an affined set of VMs. If there is no such host all the affined VMs will remain pending.
If new VMs are added to an affined role, it will pick one of the hosts where the VMs are running. By default, all should be running in the same host but if you manually migrate a VM to another host it will be considered feasible for the role.
The scheduler does not have any synchronization point with the state of the VM group, it will start scheduling pending VMs as soon as they show up.
Re-scheduling of VM Groups works as for any other VM, it will look for a different host considering the placement constraints.
Using a VM Group¶
Once you have defined your VM Group you can start adding VMs to it, by either picking a role and VM group at instantiation or by setting it in the VM Template. To apply a VM Group to your Virtual Machines either use the Sunstone wizard, or set the VM_GROUP attribute:
onetemplate update 0
...
VMGROUP = [ VMGROUP_NAME = "muilt-tier app", ROLE = "db" ]
You can also specify the VM_GROUP by its id (VMGROUP_ID), and in case of multiple groups with the same name you can select it by owner with VMGROUP_UID; as any other resource in OpenNebula.
Note
You can also add the VMGROUP attribute when a VM is created (onevm create) or when the associated template is instantiated (onetemplate instantiate). This way the same VM template can be associated with different roles.
VM Group Management¶
VM Groups can be updated to edit or add new rules. Currently only role to role rules can be updated if there are no VMs in the roles. All base operations are supported for the VMGroup object: create, delete, chgrp, chown, chmod, update, rename, list, show, lock and unlock. For managing roles use onevmgroup commands role-add, role-delete and role-update.
Note also that the same ACL/permission system is applied to VM Groups, so use access is required to place VMs in a group.
Managing VM Groups with Sunstone¶
You can also manage VM Groups using Sunstone, through the VM Group tab.